Page 96 - Reliability and Maintainability of In service Pipelines
P. 96
Methods for Structural Reliability Analysis 85
f (r)
f (sr) R
SR
f (s)
S
r
µ
R f (r,s)
RS
0
µ
S
G = 0
G>0:Safe
domain
G<0:Failure
S domain D
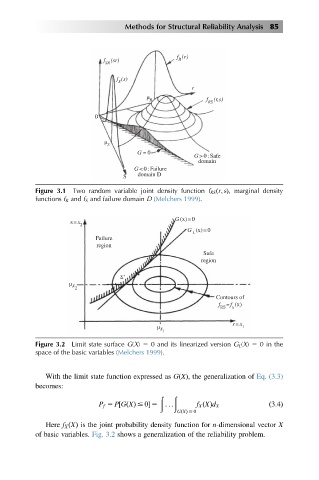
Figure 3.1 Two random variable joint density function f RS ðr; sÞ, marginal density
functions f R and f S and failure domain D (Melchers 1999).
G(x)=0
s= x
2
G (x)=0
L
Failure
region
Safe
region
x *
µ x
2
Contours of
f =f (x)
RS x
r=x
µ x 1
1
Figure 3.2 Limit state surface G(X) 5 0 and its linearized version G L (X) 5 0 in the
space of the basic variables (Melchers 1999).
With the limit state function expressed as G(X), the generalization of Eq. (3.3)
becomes:
ð ð
P f 5 P½GðXÞ # 0 5 ... f X ðXÞd X ð3:4Þ
GðXÞ # 0
Here f X ðXÞ is the joint probability density function for n-dimensional vector X
of basic variables. Fig. 3.2 shows a generalization of the reliability problem.