Page 98 - Reliability and Maintainability of In service Pipelines
P. 98
Methods for Structural Reliability Analysis 87
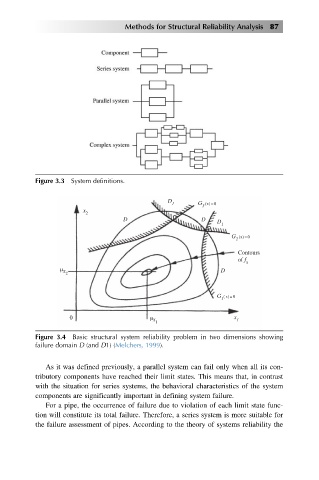
Figure 3.3 System definitions.
D
1 G (x)=0
3
x
2
D D D
1
G (x)=0
2
Contours
of f
x
µ x D
2
G (x)=0
1
0 µ x x
1 1
Figure 3.4 Basic structural system reliability problem in two dimensions showing
failure domain D (and D1) (Melchers, 1999).
As it was defined previously, a parallel system can fail only when all its con-
tributory components have reached their limit states. This means that, in contrast
with the situation for series systems, the behavioral characteristics of the system
components are significantly important in defining system failure.
For a pipe, the occurrence of failure due to violation of each limit state func-
tion will constitute its total failure. Therefore, a series system is more suitable for
the failure assessment of pipes. According to the theory of systems reliability the