Page 130 - Renewable Energy Devices and System with Simulations in MATLAB and ANSYS
P. 130
Overview of PV Maximum Power Point Tracking Techniques 117
the scanning process are continuously updated in [85] based on the geometry of the power–voltage
curve of the PV array under partial shading conditions. The calculation of the voltage windows is
performed using the value of the open-circuit voltage of the PV modules comprising the PV source,
which must be known prior to the application of this global MPPT method.
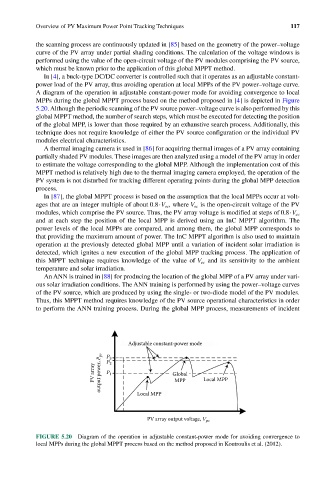
In [4], a buck-type DC/DC converter is controlled such that it operates as an adjustable constant-
power load of the PV array, thus avoiding operation at local MPPs of the PV power– voltage curve.
A diagram of the operation in adjustable constant-power mode for avoiding convergence to local
MPPs during the global MPPT process based on the method proposed in [4] is depicted in Figure
5.20. Although the periodic scanning of the PV source power–voltage curve is also performed by this
global MPPT method, the number of search steps, which must be executed for detecting the position
of the global MPP, is lower than those required by an exhaustive search process. Additionally, this
technique does not require knowledge of either the PV source configuration or the individual PV
modules electrical characteristics.
A thermal imaging camera is used in [86] for acquiring thermal images of a PV array containing
partially shaded PV modules. These images are then analyzed using a model of the PV array in order
to estimate the voltage corresponding to the global MPP. Although the implementation cost of this
MPPT method is relatively high due to the thermal imaging camera employed, the operation of the
PV system is not disturbed for tracking different operating points during the global MPP detection
process.
In [87], the global MPPT process is based on the assumption that the local MPPs occur at volt-
ages that are an integer multiple of about 0 8. ⋅V oc , where V oc is the open-circuit voltage of the PV
.
modules, which comprise the PV source. Thus, the PV array voltage is modified at steps of 0 8⋅V oc
and at each step the position of the local MPP is derived using an InC MPPT algorithm. The
power levels of the local MPPs are compared, and among them, the global MPP corresponds to
that providing the maximum amount of power. The InC MPPT algorithm is also used to maintain
operation at the previously detected global MPP until a variation of incident solar irradiation is
detected, which ignites a new execution of the global MPP tracking process. The application of
this MPPT technique requires knowledge of the value of V oc and its sensitivity to the ambient
temperature and solar irradiation.
An ANN is trained in [88] for producing the location of the global MPP of a PV array under vari-
ous solar irradiation conditions. The ANN training is performed by using the power– voltage curves
of the PV source, which are produced by using the single- or two-diode model of the PV modules.
Thus, this MPPT method requires knowledge of the PV source operational characteristics in order
to perform the ANN training process. During the global MPP process, measurements of incident
Adjustable constant-power mode
P
output power, P pv 1 Global Local MPP
3
PV array P 2
P
MPP
Local MPP
PV array output voltage, V pv
FIGURE 5.20 Diagram of the operation in adjustable constant-power mode for avoiding convergence to
local MPPs during the global MPPT process based on the method proposed in Koutroulis et al. (2012).