Page 372 - Renewable Energy Devices and System with Simulations in MATLAB and ANSYS
P. 372
Microgrid for High-Surety Power: Architectures, Controls, Protection, and Demonstration 359
Energy sources can be integrated into the system more flexible in this architecture. Besides, it intro-
duces redundancy to the architecture. It can be avoided that one centered topology failure results in
the failure of the whole system due to the inclusion of multiple centers.
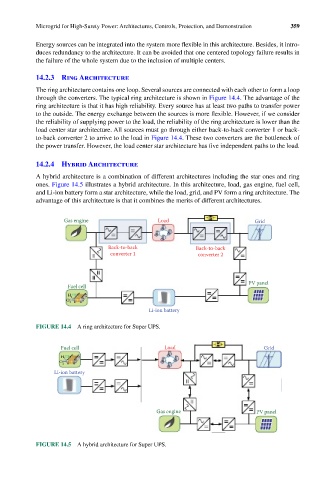
14.2.3 Ring Architecture
The ring architecture contains one loop. Several sources are connected with each other to form a loop
through the converters. The typical ring architecture is shown in Figure 14.4. The advantage of the
ring architecture is that it has high reliability. Every source has at least two paths to transfer power
to the outside. The energy exchange between the sources is more flexible. However, if we consider
the reliability of supplying power to the load, the reliability of the ring architecture is lower than the
load center star architecture. All sources must go through either back-to-back converter 1 or back-
to-back converter 2 to arrive to the load in Figure 14.4. These two converters are the bottleneck of
the power transfer. However, the load center star architecture has five independent paths to the load.
14.2.4 Hybrid Architecture
A hybrid architecture is a combination of different architectures including the star ones and ring
ones. Figure 14.5 illustrates a hybrid architecture. In this architecture, load, gas engine, fuel cell,
and Li-ion battery form a star architecture, while the load, grid, and PV form a ring architecture. The
advantage of this architecture is that it combines the merits of different architectures.
Gas engine Load Grid
Back-to-back Back-to-back
converter 1 converter 2
PV panel
Fuel cell
H 2
O 2
Li-ion battery
FIGURE 14.4 A ring architecture for Super UPS.
Fuel cell Load Grid
H 2
O 2
Li-ion battery
Gas engine PV panel
FIGURE 14.5 A hybrid architecture for Super UPS.