Page 104 - Reservoir Geomechanics
P. 104
s 1
a.
b
s n
s 3
t
b.
Mohr envelope
t
Failure occurs when: t = f(s n )
t f t = Shear stress
s = Normal stress
n
s
s = 0 s s s
3 3 n 1
s = UCS (C )
1 0
c.
Linearized Mohr envelope
t
m (coefficient of internal friction)
i
S 2b
0
s = 0 s s s
3 3 1
s = UCS (C )
1 0
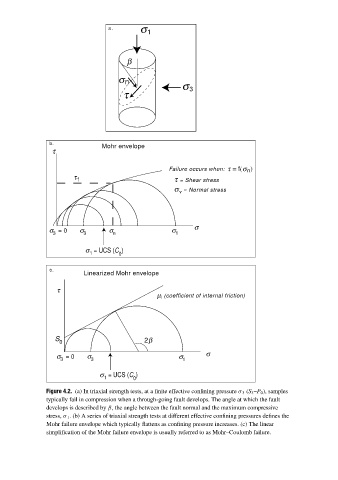
Figure 4.2. (a) In triaxial strength tests, at a finite effective confining pressure σ 3 (S 3 –P 0 ), samples
typically fail in compression when a through-going fault develops. The angle at which the fault
develops is described by β, the angle between the fault normal and the maximum compressive
stress, σ 1 . (b) A series of triaxial strength tests at different effective confining pressures defines the
Mohr failure envelope which typically flattens as confining pressure increases. (c) The linear
simplification of the Mohr failure envelope is usually referred to as Mohr–Coulomb failure.