Page 54 - Robots Androids and Animatrons : 12 Incredible Projects You Can Build
P. 54
In general
Most robotists use alkaline batteries when primary batteries are
called for and NiCd batteries when secondary batteries are needed.
Building a NiCd battery charger
NiCd battery chargers are inexpensive. Typically it is not worth
the time and effort to build a stand-alone charger for common-size
batteries such as AAA, AA, C, D, and 9V. However, if one wishes to
incorporate a built-in charger for a robot, then knowing how to build
a custom battery charger is important. While most inexpensive
chargers will charge batteries only at the C/10 rate, even after the
batteries have received a full charge (14 h), the charger we will
build will drop the current down to a C/30 rate after the batteries
are fully charged. This is the recommended procedure for charg-
ing NiCd batteries. This will help ensure a long service life to your
rechargeable battery.
The following information will allow you to design a system for
charging a custom NiCd battery pack.
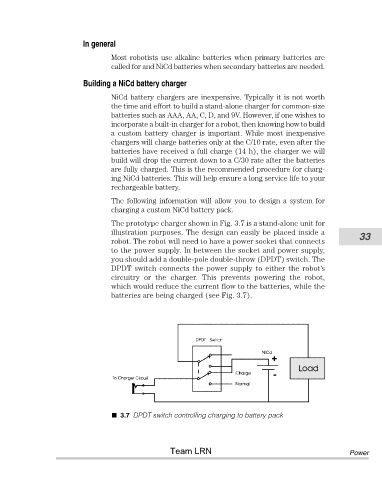
The prototype charger shown in Fig. 3.7 is a stand-alone unit for
illustration purposes. The design can easily be placed inside a 33
robot. The robot will need to have a power socket that connects
to the power supply. In between the socket and power supply,
you should add a double-pole double-throw (DPDT) switch. The
DPDT switch connects the power supply to either the robot’s
circuitry or the charger. This prevents powering the robot,
which would reduce the current flow to the batteries, while the
batteries are being charged (see Fig. 3.7).
3.7 DPDT switch controlling charging to battery pack
Team LRN Power