Page 56 - Robots Androids and Animatrons : 12 Incredible Projects You Can Build
P. 56
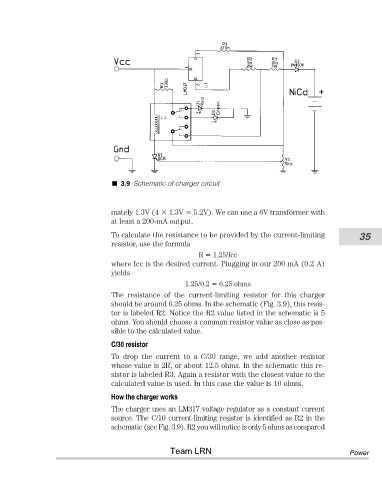
3.9 Schematic of charger circuit
mately 1.3V (4 1.3V 5.2V). We can use a 6V transformer with
at least a 200-mA output.
To calculate the resistance to be provided by the current-limiting 35
resistor, use the formula
R 1.25/Icc
where Icc is the desired current. Plugging in our 200 mA (0.2 A)
yields
1.25/0.2 6.25 ohms
The resistance of the current-limiting resistor for this charger
should be around 6.25 ohms. In the schematic (Fig. 3.9), this resis-
tor is labeled R2. Notice the R2 value listed in the schematic is 5
ohms. You should choose a common resistor value as close as pos-
sible to the calculated value.
C/30 resistor
To drop the current to a C/30 range, we add another resistor
whose value is 2R, or about 12.5 ohms. In the schematic this re-
sistor is labeled R3. Again a resistor with the closest value to the
calculated value is used. In this case the value is 10 ohms.
How the charger works
The charger uses an LM317 voltage regulator as a constant current
source. The C/10 current-limiting resistor is identified as R2 in the
schematic (see Fig. 3.9). R2 you will notice is only 5 ohms as compared
Team LRN Power