Page 55 - Robots Androids and Animatrons : 12 Incredible Projects You Can Build
P. 55
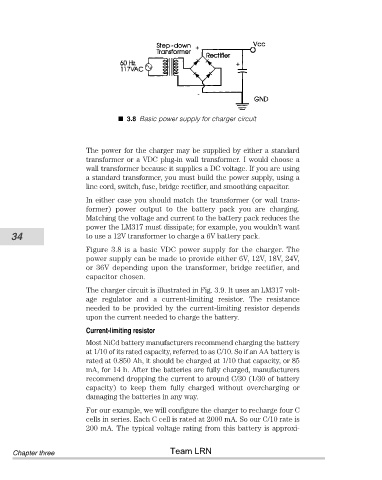
3.8 Basic power supply for charger circuit
The power for the charger may be supplied by either a standard
transformer or a VDC plug-in wall transformer. I would choose a
wall transformer because it supplies a DC voltage. If you are using
a standard transformer, you must build the power supply, using a
line cord, switch, fuse, bridge rectifier, and smoothing capacitor.
In either case you should match the transformer (or wall trans-
former) power output to the battery pack you are charging.
Matching the voltage and current to the battery pack reduces the
power the LM317 must dissipate; for example, you wouldn’t want
34 to use a 12V transformer to charge a 6V battery pack.
Figure 3.8 is a basic VDC power supply for the charger. The
power supply can be made to provide either 6V, 12V, 18V, 24V,
or 36V depending upon the transformer, bridge rectifier, and
capacitor chosen.
The charger circuit is illustrated in Fig. 3.9. It uses an LM317 volt-
age regulator and a current-limiting resistor. The resistance
needed to be provided by the current-limiting resistor depends
upon the current needed to charge the battery.
Current-limiting resistor
Most NiCd battery manufacturers recommend charging the battery
at 1/10 of its rated capacity, referred to as C/10. So if an AA battery is
rated at 0.850 Ah, it should be charged at 1/10 that capacity, or 85
mA, for 14 h. After the batteries are fully charged, manufacturers
recommend dropping the current to around C/30 (1/30 of battery
capacity) to keep them fully charged without overcharging or
damaging the batteries in any way.
For our example, we will configure the charger to recharge four C
cells in series. Each C cell is rated at 2000 mA. So our C/10 rate is
200 mA. The typical voltage rating from this battery is approxi-
Team LRN
Chapter three