Page 101 - Root Cause Failure Analysis
P. 101
92 Root Cause Failure Analysis
Configuration
Positive-displacement pumps come in a variety of configurations. Each has a specific
function and should be selected based on the effectiveness and reliability in a specific
application. The major types of positive-displacement pumps are gear, screw, vane,
and lobe.
Gear
The most common type of positive-displacement pump uses a combination of gears
and configurations to provide the liquid pressure and volume required by the applica-
tion. Variations of gear pumps are spur, helical, and herringbone.
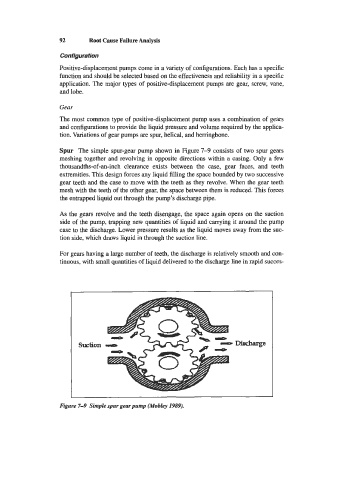
Spur The simple spur-gear pump shown in Figure 7-9 consists of two spur gears
meshing together and revolving in opposite directions within a casing. Only a few
thousandths-of-an-inch clearance exists between the case, gear faces, and teeth
extremities. This design forces any liquid filling the space bounded by two successive
gear teeth and the case to move with the teeth as they revolve. When the gear teeth
mesh with the teeth of the other gear, the space between them is reduced. This forces
the entrapped liquid out through the pump’s discharge pipe.
As the gears revolve and the teeth disengage, the space again opens on the suction
side of the pump, trapping new quantities of liquid and carrying it around the pump
case to the discharge. Lower pressure results as the liquid moves away from the suc-
tion side, which draws liquid in through the suction line.
For gears having a large number of teeth, the discharge is relatively smooth and con-
tinuous, with small quantities of liquid delivered to the discharge line in rapid succes-
Strction
I
Figure 7-9 Simple spur gear pump (Mobky 1989).