Page 77 - Root Cause Failure Analysis
P. 77
68 Root Cause Failure Analysis
To meet this requirement, a company must define an incident in terms specific to its
facility. This includes an operational definition that indicates the number of pounds of
the substance used in a particular process that would qualify as a “catastrophic” event.
Defining an incident in site-specific terms also includes defining the term could rea-
sonably have resulted in. Appendix C of the regulation provides guidelines for clari-
fying this point. It includes definitions of near misses in which a catastrophic failure
occurred but a chemical release did not occur. Clear guidelines should be established
that provide the employee with a quantifiable means of defining those incidents that
require a violation report.
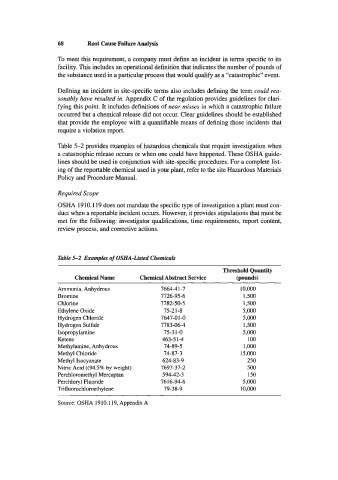
Table 5-2 provides examples of hazardous chemicals that require investigation when
a catastrophic release occurs or when one could have happened. These OSHA guide-
lines should be used in conjunction with site-specific procedures. For a complete list-
ing of the reportable chemical used in your plant, refer to the site Hazardous Materials
Policy and Procedure Manual.
Required Scope
OSHA 1910.1 19 does not mandate the specific type of investigation a plant must con-
duct when a reportable incident occurs. However, it provides stipulations that must be
met for the following: investigator qualifications, time requirements, report content,
review process, and corrective actions.
Table 5-2 Examples of OSHA-Lkted Chemicals
Threshold Quantity
Chemical Name Chemical Abstract Service bounds)
Ammonia, Anhydrous 7664-41-7 10,000
Bromine 7726-95-6 1,500
Chlorine 7782-50-5 1,500
Ethylene Oxide 75-21-8 5,000
Hydrogen Chloride 7647-01 -0 5,000
Hydrogen Sulfide 7783-06-4 1,500
Isopropylamine 75-3 1-0 5.000
Ketene 463-51-4 100
Methylamine, Anhydrous 74-89-5 1 ,000
Methyl Chloride 74-87-3 15,000
Methyl Isocyanate 624-83-9 250
Nitric Acid ((94.5% by weight) 7697-37-2 500
Perchloromethyl Mercaptan 594-42-3 150
Perchloryl Fluoride 7616-94-6 5,000
Tri fluorochloroethy lene 79-38-9 10,000
Source: OSHA 1910.1 19, Appendix A