Page 435 - Satellite Communications, Fourth Edition
P. 435
Interference 415
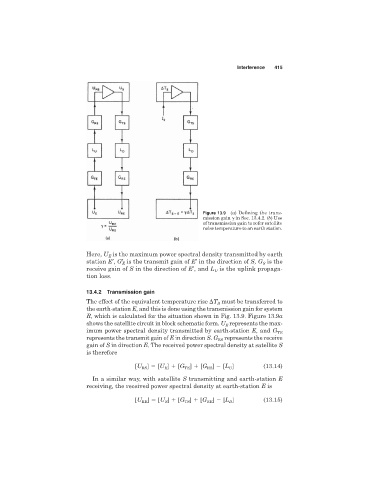
Figure 13.9 (a) Defining the trans-
mission gain in Sec. 13.4.2. (b) Use
of transmission gain to refer satellite
noise temperature to an earth station.
Here, U is the maximum power spectral density transmitted by earth
E
station E′, G′ is the transmit gain of E′ in the direction of S, G is the
E
S
receive gain of S in the direction of E′, and L is the uplink propaga-
U
tion loss.
13.4.2 Transmission gain
The effect of the equivalent temperature rise T S must be transferred to
the earth-station E, and this is done using the transmission gain for system
R, which is calculated for the situation shown in Fig. 13.9. Figure 13.9a
shows the satellite circuit in block schematic form. U represents the max-
E
imum power spectral density transmitted by earth-station E, and G TE
represents the transmit gain of E in direction S. G RS represents the receive
gain of S in direction E. The received power spectral density at satellite S
is therefore
[U ] [U ] [G ] [G ] [L ] (13.14)
RS
E
RS
U
TE
In a similar way, with satellite S transmitting and earth-station E
receiving, the received power spectral density at earth-station E is
[U ] [U ] [G ] [G ] [L ] (13.15)
D
RE
RE
TS
S