Page 188 - Schaum's Outline of Differential Equations
P. 188
CHAP. 18] GRAPHICAL METHODS FOR SOLVING DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 171
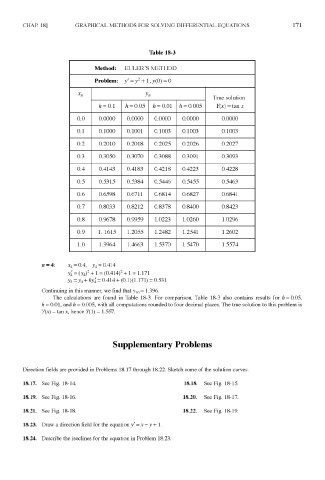
Table 18-3
Method: EULER'S METHOD
2
Problem: / = y + 1 ; y(0) = 0
y
x n n True solution
h = 0.l h = 0.05 ft = 0.01 h = 0.005 Y(x) = tan x
0.0 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000
0.1 0.1000 0.1001 0.1003 0.1003 0.1003
0.2 0.2010 0.2018 0.2025 0.2026 0.2027
0.3 0.3050 0.3070 0.3088 0.3091 0.3093
0.4 0.4143 0.4183 0.4218 0.4223 0.4228
0.5 0.5315 0.5384 0.5446 0.5455 0.5463
0.6 0.6598 0.6711 0.6814 0.6827 0.6841
0.7 0.8033 0.8212 0.8378 0.8400 0.8423
0.8 0.9678 0.9959 1.0223 1.0260 1.0296
0.9 1. 1615 1.2055 1.2482 1.2541 1.2602
1.0 1.3964 1.4663 1.5370 1.5470 1.5574
n = 4:
Continuing in this manner, we find that y w = 1.396.
The calculations are found in Table 18-3. For comparison, Table 18-3 also contains results for h = 0.05,
h = 0.01, and h = 0.005, with all computations rounded to four decimal places. The true solution to this problem is
Y(x) = tan x, hence 7(1) = 1.557.
Supplementary Problems
Direction fields are provided in Problems 18.17 through 18.22. Sketch some of the solution curves.
18.17. See Fig. 18-14. 18.18. See Fig. 18-15.
18.19. See Fig. 18-16. 18.20. See Fig. 18-17.
18.21. See Fig. 18-18. 18.22. See Fig. 18-19.
18.23. Draw a direction field for the equation y' = x - y + 1.
18.24. Describe the isoclines for the equation in Problem 18.23.