Page 209 - Schaum's Outline of Differential Equations
P. 209
192 NUMERICAL METHODS FOR SOLVING DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS [CHAP. 19
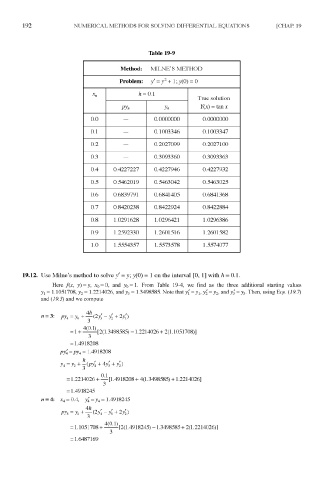
Table 19-9
Method: MILNE'S METHOD
2
Problem: / = y + 1 ; >>(0) = 0
h = 0.l
x n
True solution
py n y n Y(x) = lanx
0.0 — 0.0000000 0.0000000
0.1 — 0.1003346 0.1003347
0.2 — 0.2027099 0.2027100
0.3 — 0.3093360 0.3093363
0.4 0.4227227 0.4227946 0.4227932
0.5 0.5462019 0.5463042 0.5463025
0.6 0.6839791 0.6841405 0.6841368
0.7 0.8420238 0.8422924 0.8422884
0.8 1.0291628 1.0296421 1.0296386
0.9 1.2592330 1.2601516 1.2601582
1.0 1.5554357 1.5573578 1.5574077
19.12. Use Milne's method to solve / = y; y(0) = 1 on the interval [0, 1] with h = 0.1.
Here (x, y)=y, x 0 = 0, and yo=l. From Table 19-4, we find as the three additional starting values
f
y 1= 1.1051708, y 2= 1.2214026, and y 3 = 1.3498585. Note that y{ = yi, y 2 = y 2, and y3=y 3. Then, using Eqs. (19.7)
and (19.3) and we compute