Page 371 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Applied Physics
P. 371
356 ALTERNATING-CURRENT CIRCUITS [CHAP. 29
The negative phase angle means that the voltage across the resistor is ahead of the applied voltage, as in
Fig. 29-6(b). Equivalently we can say that the current in the circuit leads the voltage, as in Fig. 29-4(c). (We
recall that phasors rotate counterclockwise.)
IMPEDANCE
Because
V R = IR V L = IX L V C = IX C
we can rewrite the above formula for V in the form
2
V = I R + (X L − X C ) 2
The quantity
2
Z = R + (X L − X C ) 2
is called the impedance of the circuit and corresponds to the resistance of a direct-current (dc) circuit. The unit
of Z is the ohm. When an ac voltage whose frequency is f is applied to a circuit whose impedance is Z at that
frequency, the result is the current
V
I =
Z
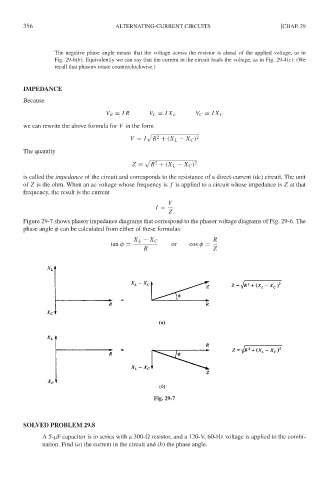
Figure 29-7 shows phasor impedance diagrams that correspond to the phasor voltage diagrams of Fig. 29-6. The
phase angle φ can be calculated from either of these formulas:
R
X L − X C
tan φ = or cos φ =
R Z
Fig. 29-7
SOLVED PROBLEM 29.8
A5-µF capacitor is in series with a 300- resistor, and a 120-V, 60-Hz voltage is applied to the combi-
nation. Find (a) the current in the circuit and (b) the phase angle.