Page 404 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Applied Physics
P. 404
CHAP. 31] SPHERICAL MIRRORS 389
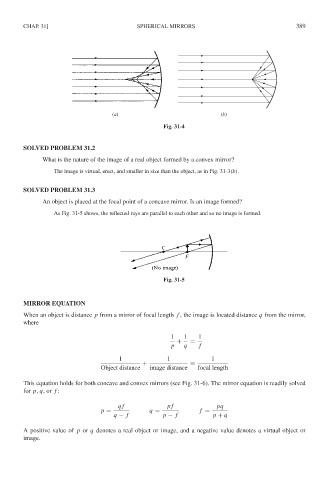
(a) (b)
Fig. 31-4
SOLVED PROBLEM 31.2
What is the nature of the image of a real object formed by a convex mirror?
The image is virtual, erect, and smaller in size than the object, as in Fig. 31-3(b).
SOLVED PROBLEM 31.3
An object is placed at the focal point of a concave mirror. Is an image formed?
As Fig. 31-5 shows, the reflected rays are parallel to each other and so no image is formed.
Fig. 31-5
MIRROR EQUATION
When an object is distance p from a mirror of focal length f , the image is located distance q from the mirror,
where
1 1 1
+ =
p q f
1 1 1
+ =
Object distance image distance focal length
This equation holds for both concave and convex mirrors (see Fig. 31-6). The mirror equation is readily solved
for p, q,or f :
q f pf pq
p = q = f =
q − f p − f p + q
A positive value of p or q denotes a real object or image, and a negative value denotes a virtual object or
image.