Page 408 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Applied Physics
P. 408
CHAP. 31] SPHERICAL MIRRORS 393
From the solution to Prob. 31.8,
f 40 cm
p = (m − 1) = (−0.267 − 1) = 190 cm
m −0.267
If we had not known that the image was inverted and had used a magnification of +0.267, the result would have
been an object distance of −110 cm. But a negative object distance signifies a virtual object, whereas here we are
given a real object, so it would be clear that the wrong sign has been used for the magnification.
SOLVED PROBLEM 31.10
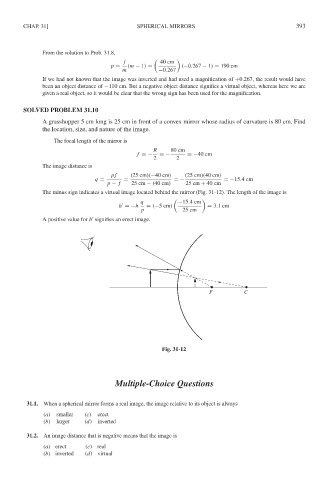
A grasshopper 5 cm long is 25 cm in front of a convex mirror whose radius of curvature is 80 cm. Find
the location, size, and nature of the image.
The focal length of the mirror is
R 80 cm
f =− =− =−40 cm
2 2
The image distance is
pf (25 cm)(−40 cm) (25 cm)(40 cm)
q = = =− =−15.4cm
p − f 25 cm − (40 cm) 25 cm + 40 cm
The minus sign indicates a virtual image located behind the mirror (Fig. 31-12). The length of the image is
q −15.4cm
h =−h = (−5cm) = 3.1cm
p 25 cm
A positive value for h signifies an erect image.
F C
Fig. 31-12
Multiple-Choice Questions
31.1. When a spherical mirror forms a real image, the image relative to its object is always
(a) smaller (c) erect
(b) larger (d) inverted
31.2. An image distance that is negative means that the image is
(a) erect (c) real
(b) inverted (d) virtual