Page 405 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Applied Physics
P. 405
390 SPHERICAL MIRRORS [CHAP. 31
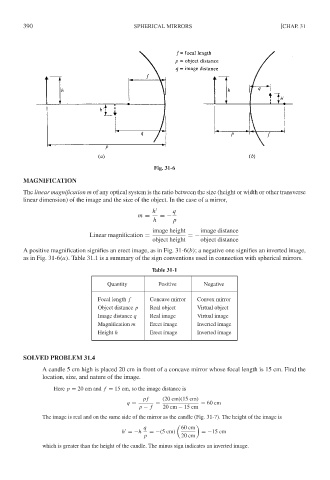
Fig. 31-6
MAGNIFICATION
The linear magnification m of any optical system is the ratio between the size (height or width or other transverse
linear dimension) of the image and the size of the object. In the case of a mirror,
h q
m = =−
h p
image height image distance
Linear magnification = =−
object height object distance
A positive magnification signifies an erect image, as in Fig. 31-6(b); a negative one signifies an inverted image,
as in Fig. 31-6(a). Table 31.1 is a summary of the sign conventions used in connection with spherical mirrors.
Table 31-1
Quantity Positive Negative
Focal length f Concave mirror Convex mirror
Object distance p Real object Virtual object
Image distance q Real image Virtual image
Magnification m Erect image Inverted image
Height h Erect image Inverted image
SOLVED PROBLEM 31.4
A candle 5 cm high is placed 20 cm in front of a concave mirror whose focal length is 15 cm. Find the
location, size, and nature of the image.
Here p = 20 cm and f = 15 cm, so the image distance is
pf (20 cm)(15 cm)
q = = = 60 cm
p − f 20 cm − 15 cm
The image is real and on the same side of the mirror as the candle (Fig. 31-7). The height of the image is
q 60 cm
h =−h =−(5cm) =−15 cm
p 20 cm
which is greater than the height of the candle. The minus sign indicates an inverted image.