Page 65 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Electric Circuits
P. 65
ANALYSIS METHODS
54
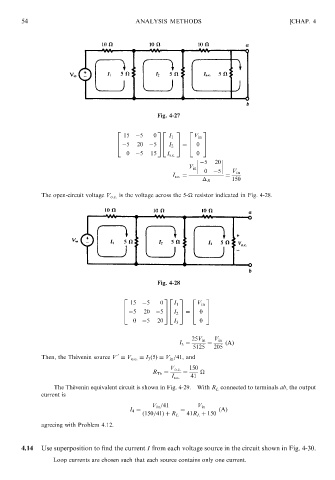
Fig. 4-27 [CHAP. 4
2 32 3 2 3
15 5 0 I 1 V in
6 76 7 6 7
4 5 20 5 54 I 2 5 ¼ 4 0 5
0 5 15 I s:c: 0
5 20
V in
0 5 V in
I s:c: ¼ ¼
R 150
The open-circuit voltage V o:c: is the voltage across the 5-
resistor indicated in Fig. 4-28.
Fig. 4-28
2 32 3 2 3
15 5 0 I 1 V in
6 76 7 6 7
4
4 5 20 5 5 I 2 5 ¼ 4 0 5
0 5 20 I 3 0
25V in V in
I 3 ¼ ¼ ðAÞ
5125 205
0
Then, the The ´ venin source V ¼ V o:c: ¼ I 3 ð5Þ¼ V in =41, and
150
V o:c:
R Th ¼ ¼
I s:c: 41
The The ´ venin equivalent circuit is shown in Fig. 4-29. With R L connected to terminals ab, the output
current is
V in =41 V in
I 4 ¼ ¼ ðAÞ
ð150=41Þþ R L 41R L þ 150
agreeing with Problem 4.12.
4.14 Use superposition to find the current I from each voltage source in the circuit shown in Fig. 4-30.
Loop currents are chosen such that each source contains only one current.