Page 60 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Electric Circuits
P. 60
ANALYSIS METHODS
CHAP. 4]
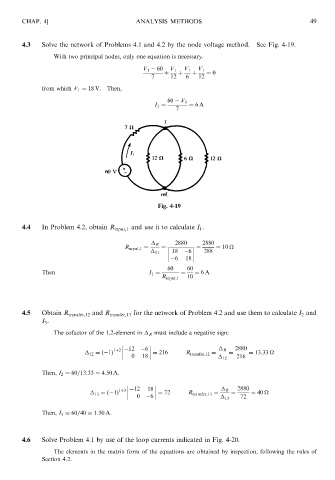
4.3 Solve the network of Problems 4.1 and 4.2 by the node voltage method. See Fig. 4-19. 49
With two principal nodes, only one equation is necessary.
V 1 60 V 1 V 1 V 1
þ þ þ ¼ 0
7 12 6 12
from which V 1 ¼ 18 V. Then,
60 V 1
I 1 ¼ ¼ 6A
7
Fig. 4-19
4.4 In Problem 4.2, obtain R input;1 and use it to calculate I 1 .
2880 2880
R
R input;1 ¼ ¼ ¼ ¼ 10
11 18 6 288
6 18
60 60
Then I 1 ¼ ¼ ¼ 6A
R input;1 10
4.5 Obtain R transfer;12 and R transfer;13 for the network of Problem 4.2 and use them to calculate I 2 and
I 3 .
The cofactor of the 1,2-element in R must include a negative sign:
1þ2 12 6 R 2880
12 ¼ð 1Þ 0 18 ¼ 216 R transfer;12 ¼ 12 ¼ 216 ¼ 13:33
Then, I 2 ¼ 60=13:33 ¼ 4:50 A:
1þ3 12 18 R 2880
13 ¼ð 1Þ 0 6 ¼ 72 R transfer;13 ¼ 13 ¼ 72 ¼ 40
Then, I 3 ¼ 60=40 ¼ 1:50 A:
4.6 Solve Problem 4.1 by use of the loop currents indicated in Fig. 4-20.
The elements in the matrix form of the equations are obtained by inspection, following the rules of
Section 4.2.