Page 58 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Electric Circuits
P. 58
47
ANALYSIS METHODS
CHAP. 4]
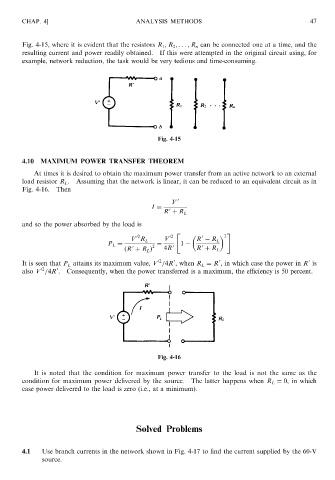
Fig. 4-15, where it is evident that the resistors R 1 ; R 2 ; ... ; R n can be connected one at a time, and the
resulting current and power readily obtained. If this were attempted in the original circuit using, for
example, network reduction, the task would be very tedious and time-consuming.
Fig. 4-15
4.10 MAXIMUM POWER TRANSFER THEOREM
At times it is desired to obtain the maximum power transfer from an active network to an external
load resistor R L . Assuming that the network is linear, it can be reduced to an equivalent circuit as in
Fig. 4-16. Then
V 0
I ¼ 0
R þ R L
and so the power absorbed by the load is
" #
02 02 0 2
V R L V R R L
P L ¼ 2 ¼ 0 1 0
0
ðR þ R L Þ 4R R þ R L
0
0
02
0
It is seen that P L attains its maximum value, V =4R , when R L ¼ R , in which case the power in R is
02
0
also V =4R . Consequently, when the power transferred is a maximum, the efficiency is 50 percent.
Fig. 4-16
It is noted that the condition for maximum power transfer to the load is not the same as the
condition for maximum power delivered by the source. The latter happens when R L ¼ 0, in which
case power delivered to the load is zero (i.e., at a minimum).
Solved Problems
4.1 Use branch currents in the network shown in Fig. 4-17 to find the current supplied by the 60-V
source.