Page 131 - Sensors and Control Systems in Manufacturing
P. 131
92
Cha p te r
T w o
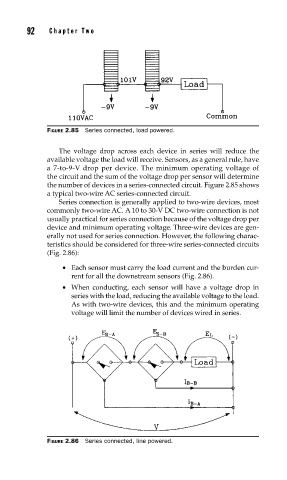
FIGURE 2.85 Series connected, load powered.
The voltage drop across each device in series will reduce the
available voltage the load will receive. Sensors, as a general rule, have
a 7-to-9-V drop per device. The minimum operating voltage of
the circuit and the sum of the voltage drop per sensor will determine
the number of devices in a series-connected circuit. Figure 2.85 shows
a typical two-wire AC series-connected circuit.
Series connection is generally applied to two-wire devices, most
commonly two-wire AC. A 10 to 30-V DC two-wire connection is not
usually practical for series connection because of the voltage drop per
device and minimum operating voltage. Three-wire devices are gen-
erally not used for series connection. However, the following charac-
teristics should be considered for three-wire series-connected circuits
(Fig. 2.86):
• Each sensor must carry the load current and the burden cur-
rent for all the downstream sensors (Fig. 2.86).
• When conducting, each sensor will have a voltage drop in
series with the load, reducing the available voltage to the load.
As with two-wire devices, this and the minimum operating
voltage will limit the number of devices wired in series.
FIGURE 2.86 Series connected, line powered.