Page 155 - Sensors and Control Systems in Manufacturing
P. 155
116
T w o
Cha p te r
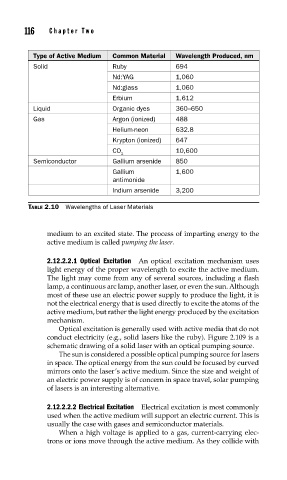
Type of Active Medium Common Material Wavelength Produced, nm
Solid Ruby 694
Nd:YAG 1,060
Nd:glass 1,060
Erbium 1,612
Liquid Organic dyes 360–650
Gas Argon (ionized) 488
Helium-neon 632.8
Krypton (ionized) 647
CO 10,600
2
Semiconductor Gallium arsenide 850
Gallium 1,600
antimonide
Indium arsenide 3,200
TABLE 2.10 Wavelengths of Laser Materials
medium to an excited state. The process of imparting energy to the
active medium is called pumping the laser.
2.12.2.2.1 Optical Excitation An optical excitation mechanism uses
light energy of the proper wavelength to excite the active medium.
The light may come from any of several sources, including a flash
lamp, a continuous arc lamp, another laser, or even the sun. Although
most of these use an electric power supply to produce the light, it is
not the electrical energy that is used directly to excite the atoms of the
active medium, but rather the light energy produced by the excitation
mechanism.
Optical excitation is generally used with active media that do not
conduct electricity (e.g., solid lasers like the ruby). Figure 2.109 is a
schematic drawing of a solid laser with an optical pumping source.
The sun is considered a possible optical pumping source for lasers
in space. The optical energy from the sun could be focused by curved
mirrors onto the laser’s active medium. Since the size and weight of
an electric power supply is of concern in space travel, solar pumping
of lasers is an interesting alternative.
2.12.2.2.2 Electrical Excitation Electrical excitation is most commonly
used when the active medium will support an electric current. This is
usually the case with gases and semiconductor materials.
When a high voltage is applied to a gas, current-carrying elec-
trons or ions move through the active medium. As they collide with