Page 186 - Sensors and Control Systems in Manufacturing
P. 186
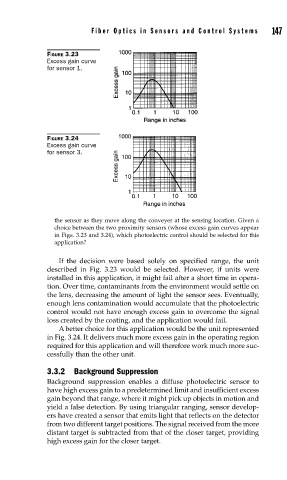
FIGURE 3.23 Fiber Optics in Sensors and Contr ol Systems 147
Excess gain curve
for sensor 1.
FIGURE 3.24
Excess gain curve
for sensor 3.
the sensor as they move along the conveyer at the sensing location. Given a
choice between the two proximity sensors (whose excess gain curves appear
in Figs. 3.23 and 3.24), which photoelectric control should be selected for this
application?
If the decision were based solely on specified range, the unit
described in Fig. 3.23 would be selected. However, if units were
installed in this application, it might fail after a short time in opera-
tion. Over time, contaminants from the environment would settle on
the lens, decreasing the amount of light the sensor sees. Eventually,
enough lens contamination would accumulate that the photoelectric
control would not have enough excess gain to overcome the signal
loss created by the coating, and the application would fail.
A better choice for this application would be the unit represented
in Fig. 3.24. It delivers much more excess gain in the operating region
required for this application and will therefore work much more suc-
cessfully than the other unit.
3.3.2 Background Suppression
Background suppression enables a diffuse photoelectric sensor to
have high excess gain to a predetermined limit and insufficient excess
gain beyond that range, where it might pick up objects in motion and
yield a false detection. By using triangular ranging, sensor develop-
ers have created a sensor that emits light that reflects on the detector
from two different target positions. The signal received from the more
distant target is subtracted from that of the closer target, providing
high excess gain for the closer target.