Page 354 - Sensors and Control Systems in Manufacturing
P. 354
Advanced Sensors in Pr ecision Manufacturing
6.23 Sensors for Hand-Eye Coordination of Microrobotic 309
Motion Utilizing Vision Technology
The micro motion of a robotic manipulator can be controlled with the
help of dual feedback by a new method that reduces position errors
by an order of magnitude. The errors—typically of the order of
centimeters—are differences between real positions on the one hand
and measured and computed positions on the other; these errors arise
from several sources in the robotic actuators and sensors and in the
kinematic model used in control computations. In comparison with
current manufacturing methods of controlling the motion of a robot
with visual feedback (the robotic equivalent of hand-eye coordina-
tion), the novel method requires neither calibration over the entire
work space nor the use of an absolute reference coordinate frame for
computing transformations between field of view and robot joint
coordinates.
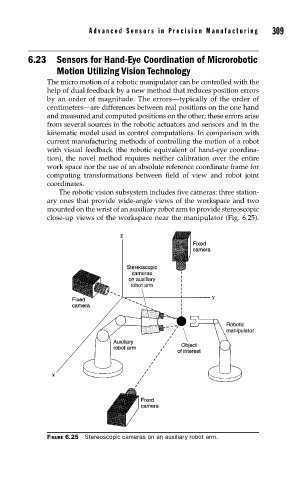
The robotic vision subsystem includes five cameras: three station-
ary ones that provide wide-angle views of the workspace and two
mounted on the wrist of an auxiliary robot arm to provide stereoscopic
close-up views of the workspace near the manipulator (Fig. 6.25).
FIGURE 6.25 Stereoscopic cameras on an auxiliary robot arm.