Page 358 - Sensors and Control Systems in Manufacturing
P. 358
Advanced Sensors in Pr ecision Manufacturing
involve thermoelasticity and shearography, have been expensive and 313
placed demands on the measured material. The optical measurement
of stress required the application of a phase coat to the object under
test. The laser diffraction method required notching or sharp mark-
ing of the specimen.
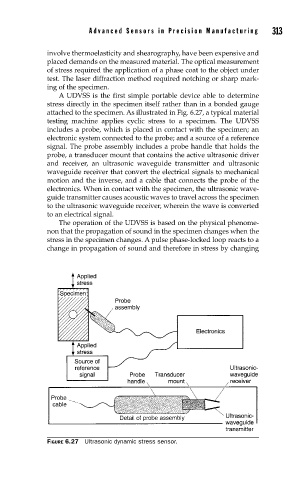
A UDVSS is the first simple portable device able to determine
stress directly in the specimen itself rather than in a bonded gauge
attached to the specimen. As illustrated in Fig. 6.27, a typical material
testing machine applies cyclic stress to a specimen. The UDVSS
includes a probe, which is placed in contact with the specimen; an
electronic system connected to the probe; and a source of a reference
signal. The probe assembly includes a probe handle that holds the
probe, a transducer mount that contains the active ultrasonic driver
and receiver, an ultrasonic waveguide transmitter and ultrasonic
waveguide receiver that convert the electrical signals to mechanical
motion and the inverse, and a cable that connects the probe of the
electronics. When in contact with the specimen, the ultrasonic wave-
guide transmitter causes acoustic waves to travel across the specimen
to the ultrasonic waveguide receiver, wherein the wave is converted
to an electrical signal.
The operation of the UDVSS is based on the physical phenome-
non that the propagation of sound in the specimen changes when the
stress in the specimen changes. A pulse phase-locked loop reacts to a
change in propagation of sound and therefore in stress by changing
FIGURE 6.27 Ultrasonic dynamic stress sensor.