Page 404 - Sensors and Control Systems in Manufacturing
P. 404
358
Cha p te r
Se v e n
An accurate method for the detection of leakage of flammable
gases such as methane (CH ), propane (C H ), and ethylene (C H ) is
4 3 8 2 4
vital in gas and petrochemical plants in order to avoid serous acci-
dents. The recent introduction of low-loss fiber into spectroscopic
measurements of these gases offers many advantages for process
control in manufacturing:
• Long-distance remote sensing
• On-line measurement and monitoring
• Low cost
• High reliability
The most commonly used method at present is to carry the sam-
ple back to the measuring laboratory for analysis; alternatively,
numerous spectrometers may be used at various points around the
factory. The new advances in spectroscopic measurements allow even
CH to be observed at a distance of 10 km with a detection sensitivity
4
as low as 5 percent of the lower explosion limit (LEL) concentration.
The optical-fiber gas measuring system employs an absorption spec-
troscopy technique, with the light passing through a gas-detection
cell for analysis. The overtone absorption bands of a number of flam-
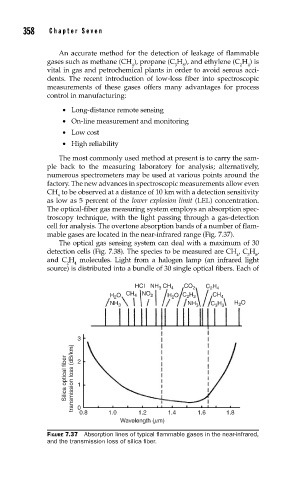
mable gases are located in the near-infrared range (Fig. 7.37).
The optical gas sensing system can deal with a maximum of 30
detection cells (Fig. 7.38). The species to be measured are CH , C H ,
4 3 8
and C H molecules. Light from a halogen lamp (an infrared light
2 4
source) is distributed into a bundle of 30 single optical fibers. Each of
HCI NH CH 4 CO 2 C H
3
2 4
H O CH 4 NO 2 H O C H CH 4
2 2
2
2
NH 3 NH 3 C H H O
2
3 3
3
Silica optical fiber transmission loss (dB/km) 2
1
0
0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8
Wavelength (mm)
FIGURE 7.37 Absorption lines of typical fl ammable gases in the near-infrared,
and the transmission loss of silica fi ber.