Page 403 - Sensors and Control Systems in Manufacturing
P. 403
Industrial Sensors and Contr ol
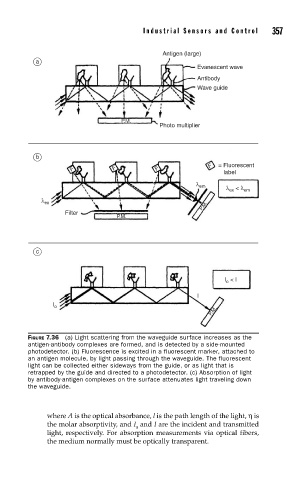
Antigen (large) 357
a
Evanescent wave
Antibody
Wave guide
P.M.
Photo multiplier
b
F F F F = Fluorescent
label
λ em λ < λ em
ex
λ ex
P .M.
Filter
P.M.
c
I < I
o
I
I o
P.M.
FIGURE 7.36 (a) Light scattering from the waveguide surface increases as the
antigen-antibody complexes are formed, and is detected by a side-mounted
photodetector. (b) Fluorescence is excited in a fluorescent marker, attached to
an antigen molecule, by light passing through the waveguide. The fluorescent
light can be collected either sideways from the guide, or as light that is
retrapped by the guide and directed to a photodetector. (c) Absorption of light
by antibody-antigen complexes on the surface attenuates light traveling down
the waveguide.
where A is the optical absorbance, l is the path length of the light, η is
the molar absorptivity, and I and I are the incident and transmitted
0
light, respectively. For absorption measurements via optical fibers,
the medium normally must be optically transparent.