Page 399 - Sensors and Control Systems in Manufacturing
P. 399
Industrial Sensors and Contr ol
7.16.2 Liquid Level Sensors in Manufacturing Process 353
Control for Petroleum and Chemical Plants
Several optical-fiber liquid level sensors developed in recent years
have been based on direct interaction between the light and liquid.
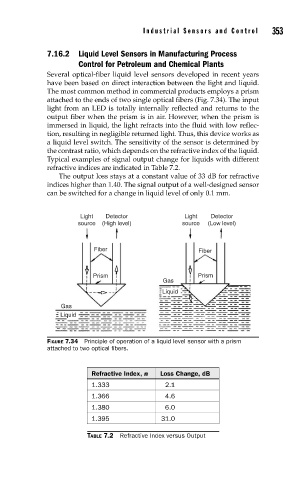
The most common method in commercial products employs a prism
attached to the ends of two single optical fibers (Fig. 7.34). The input
light from an LED is totally internally reflected and returns to the
output fiber when the prism is in air. However, when the prism is
immersed in liquid, the light refracts into the fluid with low reflec-
tion, resulting in negligible returned light. Thus, this device works as
a liquid level switch. The sensitivity of the sensor is determined by
the contrast ratio, which depends on the refractive index of the liquid.
Typical examples of signal output change for liquids with different
refractive indices are indicated in Table 7.2.
The output loss stays at a constant value of 33 dB for refractive
indices higher than 1.40. The signal output of a well-designed sensor
can be switched for a change in liquid level of only 0.1 mm.
Light Detector Light Detector
source (High level) source (Low level)
Fiber Fiber
Prism Prism
Gas
Liquid
Gas
Liquid
FIGURE 7.34 Principle of operation of a liquid level sensor with a prism
attached to two optical fi bers.
Refractive Index, n Loss Change, dB
1.333 2.1
1.366 4.6
1.380 6.0
1.395 31.0
TABLE 7.2 Refractive Index versus Output