Page 153 - Shale Shakers Drilling Fluid Systems
P. 153
136 SHALE SHAKERS AND DRILLING FLUID SYSTEMS
Materials of Construction
The material used to weave the cloth screens
is quite varied. Screens are made from metal wires,
plastic wires, and molded plastic cloths.
Metals. The alloys that are most weavable and re-
sistant to corrosion are nickel/chrome steels: 304,
316, and 316L. These alloy wires are available in
sizes as low as 20 microns. The finest wire avail-
able is 304L, which is available as low as 16 mi-
crons. Other materials, including phosphor bronze,
brass, copper, monel, nickel, aluminum alloys,
plain steel, and plated steel are also available.
Within the drilling industry, 304 stainless cloth is
most widely used.
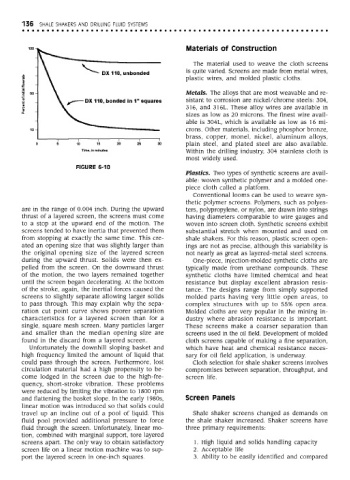
FIGURE 6-10
Plastics. Two types of synthetic screens are avail-
able: woven synthetic polymer and a molded one-
piece cloth called a platform.
Conventional looms can be used to weave syn-
thetic polymer screens. Polymers, such as polyes-
are in the range of 0.004 inch. During the upward ters, polypropylene, or nylon, are drawn into strings
thrust of a layered screen, the screens must come having diameters comparable to wire gauges and
to a stop at the upward end of the motion. The woven into screen cloth. Synthetic screens exhibit
screens tended to have inertia that prevented them substantial stretch when mounted and used on
from stopping at exactly the same time. This cre- shale shakers. For this reason, plastic screen open-
ated an opening size that was slightly larger than ings are not as precise, although this variability is
the original opening size of the layered screen not nearly as great as layered-metal steel screens.
during the upward thrust. Solids were then ex- One-piece, injection-molded synthetic cloths are
pelled from the screen. On the downward thrust typically made from urethane compounds. These
of the motion, the two layers remained together synthetic cloths have limited chemical and heat
until the screen began decelerating. At the bottom resistance but display excellent abrasion resis-
of the stroke, again, the inertial forces caused the tance. The designs range from simply supported
screens to slightly separate allowing larger solids molded parts having very little open areas, to
to pass through. This may explain why the sepa- complex structures with up to 55% open area.
ration cut point curve shows poorer separation Molded cloths are very popular in the mining in-
characteristics for a layered screen than for a dustry where abrasion resistance is important.
single, square mesh screen. Many particles larger These screens make a coarser separation than
and smaller than the median opening size are screens used in the oil field. Development of molded
found in the discard from a layered screen. cloth screens capable of making a fine separation,
Unfortunately the downhill sloping basket and which have heat and chemical resistance neces-
high frequency limited the amount of liquid that sary for oil field application, is underway.
could pass through the screen. Furthermore, lost Cloth selection for shale shaker screens involves
circulation material had a high propensity to be- compromises between separation, throughput, and
come lodged in the screen due to the high-fre- screen life.
quency, short-stroke vibration. These problems
were reduced by limiting the vibration to 1800 rpm
and flattening the basket slope. In the early 1980s, Screen Panels
linear motion was introduced so that solids could
travel up an incline out of a pool of liquid. This Shale shaker screens changed as demands on
fluid pool provided additional pressure to force the shale shaker increased. Shaker screens have
fluid through the screen. Unfortunately, linear mo- three primary requirements:
tion, combined with marginal support, tore layered
screens apart. The only way to obtain satisfactory 1. High liquid and solids handling capacity
screen life on a linear motion machine was to sup- 2. Acceptable life
port the layered screen in one-inch squares. 3. Ability to be easily identified and compared