Page 552 - Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design
P. 552
bud29281_ch10_517-568.qxd 12/16/2009 7:14 pm Page 526 pinnacle 203:MHDQ196:bud29281:0073529281:bud29281_pagefiles:
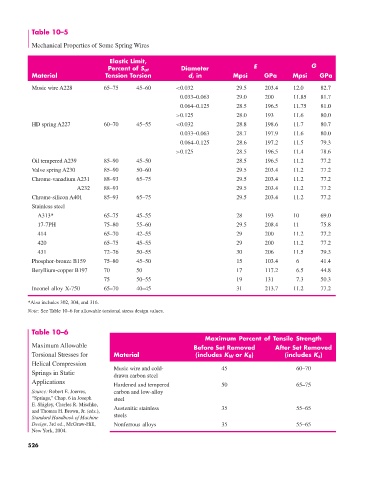
Table 10–5
Mechanical Properties of Some Spring Wires
Elastic Limit,
Percent of S ut Diameter E G
Material Tension Torsion d, in Mpsi GPa Mpsi GPa
Music wire A228 65–75 45–60 <0.032 29.5 203.4 12.0 82.7
0.033–0.063 29.0 200 11.85 81.7
0.064–0.125 28.5 196.5 11.75 81.0
>0.125 28.0 193 11.6 80.0
HD spring A227 60–70 45–55 <0.032 28.8 198.6 11.7 80.7
0.033–0.063 28.7 197.9 11.6 80.0
0.064–0.125 28.6 197.2 11.5 79.3
>0.125 28.5 196.5 11.4 78.6
Oil tempered A239 85–90 45–50 28.5 196.5 11.2 77.2
Valve spring A230 85–90 50–60 29.5 203.4 11.2 77.2
Chrome-vanadium A231 88–93 65–75 29.5 203.4 11.2 77.2
A232 88–93 29.5 203.4 11.2 77.2
Chrome-silicon A401 85–93 65–75 29.5 203.4 11.2 77.2
Stainless steel
A313* 65–75 45–55 28 193 10 69.0
17-7PH 75–80 55–60 29.5 208.4 11 75.8
414 65–70 42–55 29 200 11.2 77.2
420 65–75 45–55 29 200 11.2 77.2
431 72–76 50–55 30 206 11.5 79.3
Phosphor-bronze B159 75–80 45–50 15 103.4 6 41.4
Beryllium-copper B197 70 50 17 117.2 6.5 44.8
75 50–55 19 131 7.3 50.3
Inconel alloy X-750 65–70 40–45 31 213.7 11.2 77.2
*Also includes 302, 304, and 316.
Note: See Table 10–6 for allowable torsional stress design values.
Table 10–6
Maximum Percent of Tensile Strength
Maximum Allowable Before Set Removed After Set Removed
Torsional Stresses for Material (includes K W or K B) (includes K s)
Helical Compression
Springs in Static Music wire and cold- 45 60–70
drawn carbon steel
Applications Hardened and tempered 50 65–75
Source: Robert E. Joerres, carbon and low-alloy
“Springs,” Chap. 6 in Joseph steel
E. Shigley, Charles R. Mischke, Austenitic stainless 35 55–65
and Thomas H. Brown, Jr. (eds.),
Standard Handbook of Machine steels
Design, 3rd ed., McGraw-Hill, Nonferrous alloys 35 55–65
New York, 2004.
526