Page 362 - Six Sigma Demystified
P. 362
342 Six SigMa DemystifieD
The number of samples, personnel, and trials can vary from case to case, but in
any case, multiple trials are needed to estimate repeatability, and multiple per-
sonnel are needed to estimate reproducibility. Larger sample sizes provide bet-
ter estimates of repeatability and reproducibility, as well as overall sample
variation, but offer diminishing return given the cost of the exercise. The typical
study outlined above is usually sufficient.
When you conduct an R&R study, keep these things in mind:
• Use actual samples from operations (see above).
• Randomize the order of the samples presented to each appraiser.
• Number each sample, but try to keep this “blind” to the appraiser. (Some
appraisers have astounding memories!)
R&R Analysis
Minitab
Data input: Enter columns for part/item designator, appraiser name, and mea-
sured value.
Menu: Stat\Quality Tools\Gage Study\Gage R&R Study (Crossed); set ANOVA
analysis method.
Options: Enter specifications and historical standard deviation (from SPC anal-
ysis); use default α = 0.25 to remove the interaction term.
Results
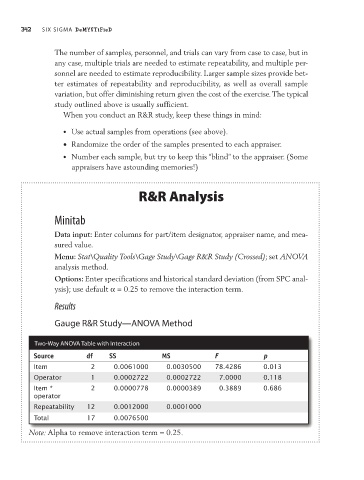
gauge R&R Study—aNOVa Method
Two-Way aNOVa Table with interaction
Source df SS MS F p
Item 2 0.0061000 0.0030500 78.4286 0.013
Operator 1 0.0002722 0.0002722 7.0000 0.118
Item * 2 0.0000778 0.0000389 0.3889 0.686
operator
Repeatability 12 0.0012000 0.0001000
Total 17 0.0076500
Note: Alpha to remove interaction term = 0.25.