Page 184 -
P. 184
CHAPTER 6 RISK ANALYSIS AND MANAGEMENT 155
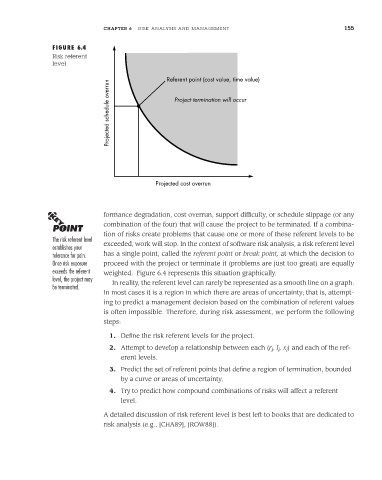
FIGURE 6.4
Risk referent
level
Referent point (cost value, time value)
Projected schedule overrun Project termination will occur
Projected cost overrun
formance degradation, cost overrun, support difficulty, or schedule slippage (or any
combination of the four) that will cause the project to be terminated. If a combina-
tion of risks create problems that cause one or more of these referent levels to be
The risk referent level
establishes your exceeded, work will stop. In the context of software risk analysis, a risk referent level
tolerance for pain. has a single point, called the referent point or break point, at which the decision to
Once risk exposure proceed with the project or terminate it (problems are just too great) are equally
exceeds the referent weighted. Figure 6.4 represents this situation graphically.
level, the project may In reality, the referent level can rarely be represented as a smooth line on a graph.
be terminated.
In most cases it is a region in which there are areas of uncertainty; that is, attempt-
ing to predict a management decision based on the combination of referent values
is often impossible. Therefore, during risk assessment, we perform the following
steps:
1. Define the risk referent levels for the project.
2. Attempt to develop a relationship between each (r , l , x ) and each of the ref-
i
i
i
erent levels.
3. Predict the set of referent points that define a region of termination, bounded
by a curve or areas of uncertainty.
4. Try to predict how compound combinations of risks will affect a referent
level.
A detailed discussion of risk referent level is best left to books that are dedicated to
risk analysis (e.g., [CHA89], [ROW88]).