Page 213 -
P. 213
11 - PROJECT RISK MANAGEMENT
product is called the risk exposure. A project manager or assigned risk manager may assign both an unmitigated
risk exposure and a mitigated risk exposure, along with the cost of risk mitigation. Risk leverage factors (the
difference between unmitigated and mitigated risk exposures divided by the cost of risk mitigation) can be used to
evaluate the effectiveness of various risk reduction strategies. See also Figure 11-11 in the PMBOK Guide.
®
Risk exposure (probability × impact) can be used to calculate monetary value as follows:
Risk expected monetary value = Risk probability (0.0 − 1.0) × Risk impact (in monetary units)
A software project thus has a quantitative value (cost or benefit) for each risk mitigation activity in comparison
to the cost and value of new work. For example, assume there is a risk of having an inadequate reporting tool in
place (assume $0 future cost for the existing tool), which could be completely mitigated by buying and using a
high-performance reporting engine that costs $10,000 to buy, implement, and run. If the project estimates that
there is a 50% chance of needing this tool, then the evaluated cost (or economic value) of purchasing the new tool
is $5,000 (0.5 × $10,000).
On the other hand, even though the existing tool has a zero cost for use, suppose that the cost of staff time
over the same period to collect and analyze data and compile reports is estimated to be $25,000 and, based on
experience, there is again a 50% chance that reports will not be usable or ready on time. The cost of continuing 11
with the existing tool is $12,500; therefore, purchasing the new tool is the better value.
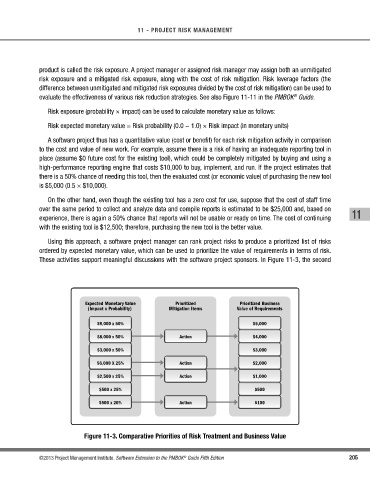
Using this approach, a software project manager can rank project risks to produce a prioritized list of risks
ordered by expected monetary value, which can be used to prioritize the value of requirements in terms of risk.
These activities support meaningful discussions with the software project sponsors. In Figure 11-3, the second
Expected Monetary Value Prioritized Prioritized Business
(Impact x Probability) Mitigation Items Value of Requirements
$9,000 x 50% $5,000
$8,000 x 50% Action $4,000
$3,000 x 50% $3,000
$6,000 X 25% Action $2,000
$2,500 x 25% Action $1,000
$500 x 25% $500
$500 x 20% Action $100
Figure 11-3. Comparative Priorities of Risk Treatment and Business Value
©2013 Project Management Institute. Software Extension to the PMBOK Guide Fifth Edition 205
®