Page 320 - Software and Systems Requirements Engineering in Practice
P. 320
282 S o f t w a r e & S y s t e m s R e q u i r e m e n t s E n g i n e e r i n g : I n P r a c t i c e
Has possible
Take X-Ray of hazard Hyperlink
Patient
Possible overdose
X-Ray Machine
Hazard Analysis
Includes Includes
Automatic,
Based on Patient Manually
Information Set Time
Has mitigation
Impacts Impacts
Interlock to prevent
overdose to patient
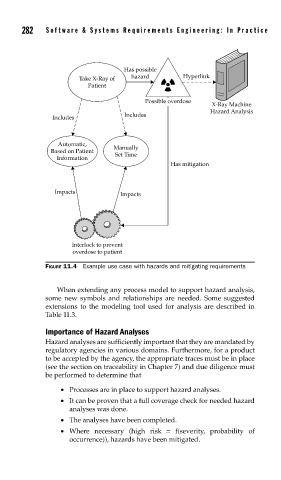
FIGURE 11.4 Example use case with hazards and mitigating requirements
When extending any process model to support hazard analysis,
some new symbols and relationships are needed. Some suggested
extensions to the modeling tool used for analysis are described in
Table 11.3.
Importance of Hazard Analyses
Hazard analyses are sufficiently important that they are mandated by
regulatory agencies in various domains. Furthermore, for a product
to be accepted by the agency, the appropriate traces must be in place
(see the section on traceability in Chapter 7) and due diligence must
be performed to determine that
• Processes are in place to support hazard analyses.
• It can be proven that a full coverage check for needed hazard
analyses was done.
• The analyses have been completed.
• Where necessary (high risk = f(severity, probability of
occurrence)), hazards have been mitigated.