Page 227 - Soil and water contamination, 2nd edition
P. 227
214 Soil and Water Contamination
0
C/CC/C
C/C = 1.0
= 1.0
= 1.0
0 0 0
5
10
15
Depth
20
25
C/C = 0.5
30 0
6642 6642 6642 35
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350
Horizontal distance
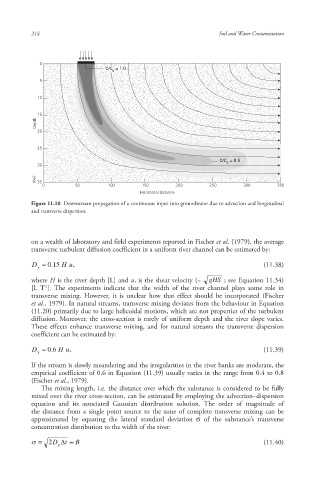
Figure 11.10 Downstream propagation of a continuous input into groundwater due to advection and longitudinal
and transverse dispersion.
on a wealth of laboratory and field experiments reported in Fischer et al. (1979), the average
transverse turbulent diffusion coefficient in a uniform river channel can be estimated by:
D . 0 15 H u (11.38)
y *
where H is the river depth [L] and u is the shear velocity (= gHS ; see Equation 11.34)
*
-1
[L T ]. The experiments indicate that the width of the river channel plays some role in
transverse mixing. However, it is unclear how that effect should be incorporated (Fischer
et al., 1979). In natural streams, transverse mixing deviates from the behaviour in Equation
(11.20) primarily due to large helicoidal motions, which are not properties of the turbulent
diffusion . Moreover, the cross-section is rarely of uniform depth and the river slope varies.
These effects enhance transverse mixing, and for natural streams the transverse dispersion
coefficient can be estimated by:
D 6 . 0 H u (11.39)
y *
If the stream is slowly meandering and the irregularities in the river banks are moderate, the
empirical coefficient of 0.6 in Equation (11.39) usually varies in the range from 0.4 to 0.8
(Fischer et al., 1979).
The mixing length , i.e. the distance over which the substance is considered to be fully
mixed over the river cross-section, can be estimated by employing the advection –dispersion
equation and its associated Gaussian distribution solution. The order of magnitude of
the distance from a single point source to the zone of complete transverse mixing can be
approximated by equating the lateral standard deviation σ of the substance’s transverse
concentration distribution to the width of the river:
2 D t B (11.40)
y
10/1/2013 6:44:59 PM
Soil and Water.indd 226 10/1/2013 6:44:59 PM
Soil and Water.indd 226