Page 283 - Solar Power in Building Design The Engineer's Complete Design Resource
P. 283
250 ECONOMICS OF SOLAR POWER SYSTEMS
array templates then can be used to establish a desirable output of dc power. Note that,
when laying blocks of PV arrays, consideration must be given to the desirable tilt
inclination to avoid cross shadowing. In some instances, the designer must also
consider trading solar power output efficiency to maximize the power output produc-
tion. As mentioned in Chapter 2, the most desirable mounting position for a PV mod-
ule to realize maximum solar insolation is the latitude minus 10 degrees. For example,
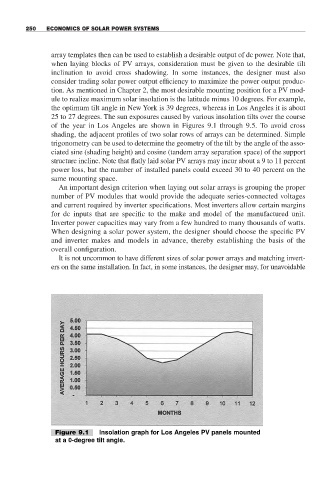
the optimum tilt angle in New York is 39 degrees, whereas in Los Angeles it is about
25 to 27 degrees. The sun exposures caused by various insolation tilts over the course
of the year in Los Angeles are shown in Figures 9.1 through 9.5. To avoid cross
shading, the adjacent profiles of two solar rows of arrays can be determined. Simple
trigonometry can be used to determine the geometry of the tilt by the angle of the asso-
ciated sine (shading height) and cosine (tandem array separation space) of the support
structure incline. Note that flatly laid solar PV arrays may incur about a 9 to 11 percent
power loss, but the number of installed panels could exceed 30 to 40 percent on the
same mounting space.
An important design criterion when laying out solar arrays is grouping the proper
number of PV modules that would provide the adequate series-connected voltages
and current required by inverter specifications. Most inverters allow certain margins
for dc inputs that are specific to the make and model of the manufactured unit.
Inverter power capacities may vary from a few hundred to many thousands of watts.
When designing a solar power system, the designer should choose the specific PV
and inverter makes and models in advance, thereby establishing the basis of the
overall configuration.
It is not uncommon to have different sizes of solar power arrays and matching invert-
ers on the same installation. In fact, in some instances, the designer may, for unavoidable
Figure 9.1 Insolation graph for Los Angeles PV panels mounted
at a 0-degree tilt angle.