Page 387 - Solid Waste Analysis and Minimization a Systems Approach
P. 387
CONSTRAINTS AND CONSIDERATIONS 365
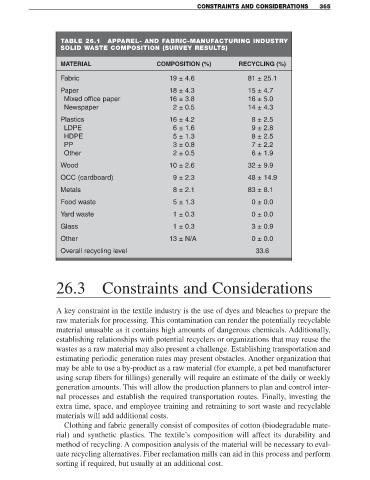
TABLE 26.1 APPAREL- AND FABRIC-MANUFACTURING INDUSTRY
SOLID WASTE COMPOSITION (SURVEY RESULTS)
MATERIAL COMPOSITION (%) RECYCLING (%)
Fabric 19 ± 4.6 81 ± 25.1
Paper 18 ± 4.3 15 ± 4.7
Mixed office paper 16 ± 3.8 16 ± 5.0
Newspaper 2 ± 0.5 14 ± 4.3
Plastics 16 ± 4.2 8 ± 2.5
LDPE 6 ± 1.6 9 ± 2.8
HDPE 5 ± 1.3 8 ± 2.5
PP 3 ± 0.8 7 ± 2.2
Other 2 ± 0.5 6 ± 1.9
Wood 10 ± 2.6 32 ± 9.9
OCC (cardboard) 9 ± 2.3 48 ± 14.9
Metals 8 ± 2.1 83 ± 8.1
Food waste 5 ± 1.3 0 ± 0.0
Yard waste 1 ± 0.3 0 ± 0.0
Glass 1 ± 0.3 3 ± 0.9
Other 13 ± N/A 0 ± 0.0
Overall recycling level 33.6
26.3 Constraints and Considerations
A key constraint in the textile industry is the use of dyes and bleaches to prepare the
raw materials for processing. This contamination can render the potentially recyclable
material unusable as it contains high amounts of dangerous chemicals. Additionally,
establishing relationships with potential recyclers or organizations that may reuse the
wastes as a raw material may also present a challenge. Establishing transportation and
estimating periodic generation rates may present obstacles. Another organization that
may be able to use a by-product as a raw material (for example, a pet bed manufacturer
using scrap fibers for fillings) generally will require an estimate of the daily or weekly
generation amounts. This will allow the production planners to plan and control inter-
nal processes and establish the required transportation routes. Finally, investing the
extra time, space, and employee training and retraining to sort waste and recyclable
materials will add additional costs.
Clothing and fabric generally consist of composites of cotton (biodegradable mate-
rial) and synthetic plastics. The textile’s composition will affect its durability and
method of recycling. A composition analysis of the material will be necessary to eval-
uate recycling alternatives. Fiber reclamation mills can aid in this process and perform
sorting if required, but usually at an additional cost.