Page 156 - Standard Handbook Of Petroleum & Natural Gas Engineering
P. 156
Basic Mechanics (Statics and Dynamics) 141
where XM4 is the sum of the vector moments of all the forces acting on the body
about any arbitrarily selected point A. In two dimensions this constitutes an algebraic
equation because all moments must act about an axis perpendicular to the plane of
the forces. In three dimensions the moments must be decomposed into components
parallel to the principal axes, and the components along each axis must sum
algebraically to zero.
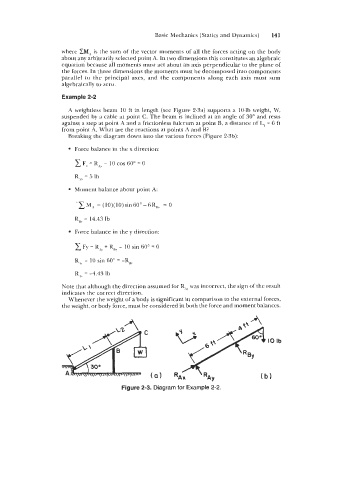
Example 2-2
A weightless beam 10 ft in length (see Figure 2-3a) supports a 10-lb weight, W,
suspended by a cable at point C. The beam is inclined at an angle of 30" and rests
against a step at point A and a frictionless fulcrum at point B, a distance of L, = 6 ft
from point A. What are the reactions at points A and B?
Breaking the diagram down into the various forces (Figure 2-3b):
Force balance in the x direction:
Fx = RA, - 10 cos 60" = 0
R<\ = 5 lb
Moment balance about point A:
'ZM, = (10)(10)sin6O0-6R,, = 0
RI%, = 14.43 lb
Force balance in the y direction:
Fy = R,, + R,\\ - 10 sin 60" = 0
R,, - 10 sin 60" = -R,,
R, = -4.43 Ib
Note that although the direction assumed for R,4, was incorrect, the sign of the result
indicates the correct direction.
Whenever the weight of a body is significant in comparison to the external forces,
the weight, or body force, must be considered in both the force and moment balances.
Figure 2-3. Diagram for Example 2-2.