Page 401 - Standard Handbook Petroleum Natural Gas Engineering VOLUME2
P. 401
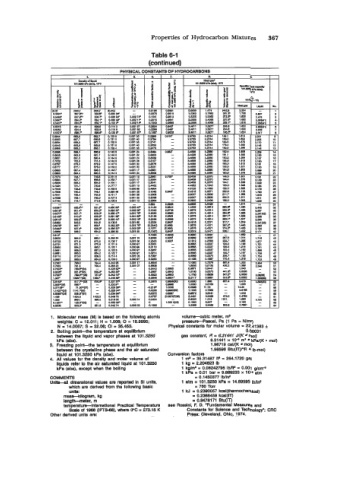
Properties of Hydrocarbon Mixtures 367
Table 6-1
(continued)
E -
- -
5
It - 15%
Ip*blw
P
1 css IS, g! LvI - .c4 LWd -
11
ld..I#- -
la
-
-
E5 - '3 ::E 3.807 1 2
0.088 w om 74* nzt 1.826 2.478 3
0.088 10* 090211b 191.8 1.m 22dW41I 4
5
am s? omll 2pO.lh 1.81(1 -
LLII*8 om 57 WE8 1822 2239 6
2W411
l.m
m(1
7
-
ai116 om 82 6 -
5 lw6.C la24 2317
om 870
aim8 om 86 182.1 lM3 2251 10 8
2.m
0.1SlO om 40 leas 1802
lm
0.1268 om 86 183.6 1.m 2.170 11
170.4
13 -
2.148
12
-
OSGl 40
0.131 8
- 1628 1.6w -
2.146
om 86
01I4
0.1458 am 162.4 lam 2- 14
0.1488 0.m 22 181.1 1.96 2.1w 16
0.1441 Mol 21 183.2 1.584 2.137 16
17
0.1428 awl 26 118 1.818 2.m
21 a
0.147 8 awl 90 1WB 1.613 16
19
0.1480 M9O isBa 1.~1 2,199 W
- 163.0 1.576 -
lea
2asS
1.m
0.1497
awl 17
21 -
2asS
aiw
MU
0.1m 6 arm 12 iaa 1.6~ 2.1~1 P
o.iw7 arm 17 lad 1.573 2.188 23
24
0.1841 arm 17 144.1 1.688 2.184
2.W
om7 am ia 1as.o 1.m 2.179 25
26
0.1BP9 am w 122.0 1.m
pP.s
0.m 49 am 26 1.185 1.m 27
0.111 7 0,001 I 211.7 in8 1.243 28
1211
28
1.811
0.1075 0.001 22 w.0 i8pl - 1898 -
iesa
-
-
0.1288 0.w113 - 30
31
om (1r 0,WSW pose ;% 2449 32
LMDg SQ 0 . OLT ~ Ea.@ 1.49 9237 85
WM 470 arm 7@ ls*;* 1- zwu) 94
aa
mr am SB" m.lh 1528
mu* 0.00216 zaw 1567 2.286 86
ai086 a001 W 217.7 lM9 2.241(431 a7
ao82w O.Wl76 m7.I lM8 22- 88
am PP am@ W42 1Am 2.124 39
- 2881 lAE? - 2.171 -
40
-
-
-
om 65
am 80
-
l.m
41
am M om 19 W.8 1.014 1.m 42
49
0.106 7 om 011 22p7 1.086 id77
0.121 9 om, 97 1WO l.lI 1.721 44 45
0.1201 Om, I i8a.u 1.m 1.741
1 .m
0.122 a Om, w 188.4 1.189 48
0,1227 Om0 97 1SZ7 1.157 1.7O8 47
1.724
48 -
48
0.1144 om 011 m7 1.181 -
ai380 - 1m 1.219 1.752
Om0 81
-
aouIps Om 17 w.4 1m 2M 60
-
awm 0.m 07 4Da2 1.988 2818 51
-
(LQIBF - 1.010 - 62
63
a06559 - 44l.B" 0.m zmiw
Om6 D - 515.9 Om2 -
-
am t8 5478 0.6360 61
1
-
-
-
09275F - 851.4 2.079 rsos(aq m
Om#- - - 1.m - 67
0- w - 14.24 - W
55
amea
omor - - -
om w - 1.w -
-
O M 78 47uI 0.4780
-
-
-
a018011 am 14 iaii. 1.86~ 41 BI
5.lsp
-
om? UP
- - 6682 0.7~1 -
ow 74
ann6 05
1. Molecular mass (M) Is based on the following atomlc volume-cublc meter, n+
weights: C = 12.011; H = 1.008; 0 I 15.9995; presaure-paecal. Pa (1 Pa = Nlm2)
N * 14.0087; S = 32.W CI = 35.453. Physical constants for molar volume = 22.41363 f
2. Bolllng poinl-the temperature at equillbdum 0.00031
between the liquid and vapor phases at 101.3260 gas constant, R = 8.31441 J/(K mol)
kPa (abs). 8.31441 x 1W ma kPa/(K - mol)
3. Freezing point-the temperature at equlllbrlum 1 .96719 caU(K mol)
between the crystalllne phase and the alr saturated 1.98598 Btu(lT)PR Ib-mol)
liquid at 101.3250 kPa (abs). Converelon factors
4. All values for the density and molar volume of 1 n+ = 35.31487 fP = 264.1720 gal
liquids refer lo the air saturated llquld at 101.3260 1 kg = 2.204629 Ib
kPa (abs), except when the bolling 1 ke/ma = 0.08242795 Ib/W = 0.001 dCfl
1 kPa = 0.01 bar = 9.669233 x 1W atm
COMMENTS = 0.1450377 IWinP
Unlts-all dimensional values are repotted in SI Unb, 1 atm = 101.3250 kPa = 14.69595 IMn*
which are dedvad from the followlng baeic = 780 Torr
unlle: 1 kJ = 0.2390057 kcal(thermochemlcal)
mase-klkgram, kg = 0.2388459 kcal(1T)
lengtkmeter, m = 0.9478171 Btu(lT)
temperatu+lnternatlonal Pradical Temperature see Rossini, F. D. 'Fundamental Measures and
Scale of 1968 (IPTS-86). where 0°C = 273.15 K Constants for Science and Technology"; CRC
Other derived units are: Press: Cleveland, Ohio, 1974.