Page 475 - Standard Handbook Petroleum Natural Gas Engineering VOLUME2
P. 475
Flow of Fluids 431
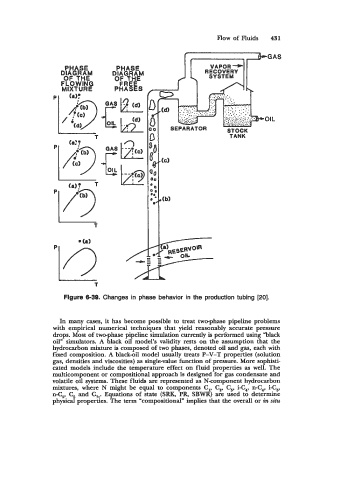
PHASE PHASE
DIAGRAM DIAGRAM
OF THE
FLOWING OF THE
MIXTURE PLRAES
Or4
00
:*; (b)
‘1/3 A
T
Figure 6-39. Changes in phase behavior in the production tubing [20].
In many cases, it has become possible to treat two-phase pipeline problems
with empirical numerical techniques that yield reasonably accurate pressure
drops. Most of two-phase pipeline simulation currently is performed using “black
oil” simulators. A black oil model’s validity rests on the assumption that the
hydrocarbon mixture is composed of two phases, denoted oil and gas, each with
fixed composition. A black-oil model usually treats P-V-T properties (solution
gas, densities and viscosities) as single-value function of pressure. More sophisti-
cated models include the temperature effect on fluid properties as well. The
multicomponent or compositional approach is designed for gas condensate and
volatile oil systems. These fluids are represented as N-component hydrocarbon
mixtures, where N might be equal to components C,, C,, C,, i-C4, n-C,, i-C,,
n-C,, C, and C,+. Equations of state (SRK, PR, SBWR) are used to determine
physical properties. The term “compositional” implies that the overall or in situ