Page 313 - Steam Turbines Design, Applications, and Rerating
P. 313
Shortcut Graphical Methods of Turbine Selection 287
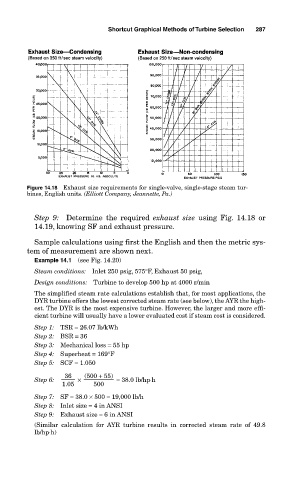
Figure 14.18 Exhaust size requirements for single-valve, single-stage steam tur-
bines, English units. (Elliott Company, Jeannette, Pa.)
Step 9: Determine the required exhaust size using Fig. 14.18 or
14.19, knowing SF and exhaust pressure.
Sample calculations using first the English and then the metric sys-
tem of measurement are shown next.
Example 14.1 (see Fig. 14.20)
Steam conditions: Inlet 250 psig, 575°F, Exhaust 50 psig,
Design conditions: Turbine to develop 500 hp at 4000 r/min
The simplified steam rate calculations establish that, for most applications, the
DYR turbine offers the lowest corrected steam rate (see below), the AYR the high-
est. The DYR is the most expensive turbine. However, the larger and more effi-
cient turbine will usually have a lower evaluated cost if steam cost is considered.
Step 1: TSR = 26.07 lb/kWh
Step 2: BSR = 36
Step 3: Mechanical loss = 55 hp
Step 4: Superheat = 169°F
Step 5: SCF = 1.050
36 (500 + 55)
Step 6: × = 38.0 lb/hp⋅h
1.05 500
Step 7: SF = 38.0 × 500 = 19,000 lb/h
Step 8: Inlet size = 4 in ANSI
Step 9: Exhaust size = 6 in ANSI
(Similar calculation for AYR turbine results in corrected steam rate of 49.8
lb/hp⋅h)