Page 315 - Steam Turbines Design, Applications, and Rerating
P. 315
Shortcut Graphical Methods of Turbine Selection 289
(c)
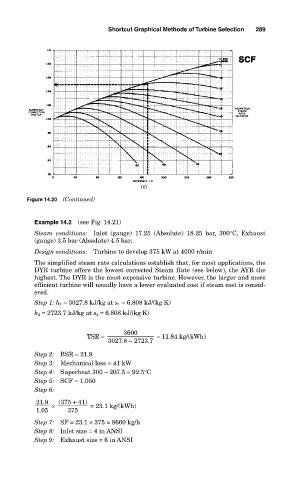
Figure 14.20 (Continued)
Example 14.2 (see Fig. 14.21)
Steam conditions: Inlet (gauge) 17.25 (Absolute) 18.25 bar, 300°C, Exhaust
(gauge) 3.5 bar (Absolute) 4.5 bar;
Design conditions: Turbine to develop 375 kW at 4000 r/min
The simplified steam rate calculations establish that, for most applications, the
DYR turbine offers the lowest corrected Steam Rate (see below), the AYR the
highest. The DYR is the most expensive turbine. However, the larger and more
efficient turbine will usually have a lower evaluated cost if steam cost is consid-
ered.
Step 1: h 1 = 3027.8 kJ/kg at s 1 = 6.808 kJ/(kg⋅K)
h 2 = 2723.7 kJ/kg at s 2 = 6.808 kJ/(kg⋅K)
3600
TSR = = 11.84 kg/(kWh)
3027.8 − 2723.7
Step 2: BSR = 21.9
Step 3: Mechanical loss = 41 kW
Step 4: Superheat 300 − 207.5 = 92.5°C
Step 5: SCF = 1.050
Step 6:
21.9 (375 + 41)
× = 23.1 kg/(kWh)
1.05 375
Step 7: SF = 23.1 × 375 = 8660 kg/h
Step 8: Inlet size = 4 in ANSI
Step 9: Exhaust size = 6 in ANSI