Page 151 -
P. 151
CHAPTER 4 • THE INTERNAL ASSESSMENT 117
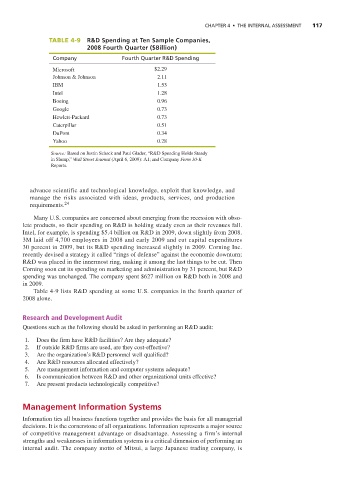
TABLE 4-9 R&D Spending at Ten Sample Companies,
2008 Fourth Quarter ($Billion)
Company Fourth Quarter R&D Spending
Microsoft $2.29
Johnson & Johnson 2.11
IBM 1.53
Intel 1.28
Boeing 0.96
Google 0.73
Hewlett-Packard 0.73
Caterpillar 0.51
DuPont 0.34
Yahoo 0.28
Source: Based on Justin Scheck and Paul Glader, “R&D Spending Holds Steady
in Slump,” Wall Street Journal (April 6, 2009): A1; and Company Form 10-K
Reports.
advance scientific and technological knowledge, exploit that knowledge, and
manage the risks associated with ideas, products, services, and production
requirements. 24
Many U.S. companies are concerned about emerging from the recession with obso-
lete products, so their spending on R&D is holding steady even as their revenues fall.
Intel, for example, is spending $5.4 billion on R&D in 2009, down slightly from 2008.
3M laid off 4,700 employees in 2008 and early 2009 and cut capital expenditures
30 percent in 2009, but its R&D spending increased slightly in 2009. Corning Inc.
recently devised a strategy it called “rings of defense” against the economic downturn;
R&D was placed in the innermost ring, making it among the last things to be cut. Then
Corning soon cut its spending on marketing and administration by 31 percent, but R&D
spending was unchanged. The company spent $627 million on R&D both in 2008 and
in 2009.
Table 4-9 lists R&D spending at some U.S. companies in the fourth quarter of
2008 alone.
Research and Development Audit
Questions such as the following should be asked in performing an R&D audit:
1. Does the firm have R&D facilities? Are they adequate?
2. If outside R&D firms are used, are they cost-effective?
3. Are the organization’s R&D personnel well qualified?
4. Are R&D resources allocated effectively?
5. Are management information and computer systems adequate?
6. Is communication between R&D and other organizational units effective?
7. Are present products technologically competitive?
Management Information Systems
Information ties all business functions together and provides the basis for all managerial
decisions. It is the cornerstone of all organizations. Information represents a major source
of competitive management advantage or disadvantage. Assessing a firm’s internal
strengths and weaknesses in information systems is a critical dimension of performing an
internal audit. The company motto of Mitsui, a large Japanese trading company, is