Page 47 - Strategies and Applications in Quantum Chemistry From Molecular Astrophysics to Molecular Engineer
P. 47
32 C. CHAVY ET AL.
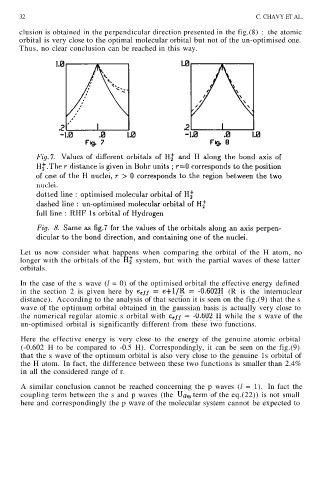
clusion is obtained in the perpendicular direction presented in the fig.(8) : the atomic
orbital is very close to the optimal molecular orbital but not of the un-optimised one.
Thus, no clear conclusion can be reached in this way.
Let us now consider what happens when comparing the orbital of the H atom, no
longer with the orbitals of the system, but with the partial waves of these latter
orbitals.
In the case of the s wave (l = 0) of the optimised orbital the effective energy defined
in the section 2 is given here by (R is the internuclear
distance). According to the analysis of that section it is seen on the fig.(9) that the s
wave of the optimum orbital obtained in the gaussian basis is actually very close to
the numerical regular atomic s orbital with while the s wave of the
un-optimised orbital is significantly different from these two functions.
Here the effective energy is very close to the energy of the genuine atomic orbital
(-0.602 H to be compared to -0.5 H). Correspondingly, it can be seen on the fig.(9)
that the s wave of the optimum orbital is also very close to the genuine 1s orbital of
the H atom. In fact, the difference between these two functions is smaller than 2.4%
in all the considered range of r.
A similar conclusion cannot be reached concerning the p waves (l = 1). In fact the
coupling term between the s and p waves (the term of the eq.(22)) is not small
here and correspondingly the p wave of the molecular system cannot be expected to