Page 183 - Structural Steel Designers Handbook AISC, AASHTO, AISI, ASTM, and ASCE-07 Design Standards
P. 183
Brockenbrough_Ch04.qxd 9/29/05 5:09 PM Page 4.11
BUILDING CODES, LOADS, AND FIRE PROTECTION*
BUILDING CODES, LOADS, AND FIRE PROTECTION 4.11
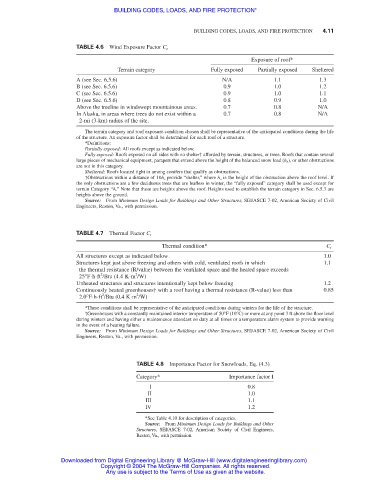
TABLE 4.6 Wind Exposure Factor C e
Exposure of roof*
Terrain category Fully exposed Partially exposed Sheltered
A (see Sec. 6.5.6) N/A 1.1 1.3
B (see Sec. 6.5.6) 0.9 1.0 1.2
C (see Sec. 6.5.6) 0.9 1.0 1.1
D (see Sec. 6.5.6) 0.8 0.9 1.0
Above the treeline in windswept mountainous areas. 0.7 0.8 N/A
In Alaska, in areas where trees do not exist within a 0.7 0.8 N/A
2-mi (3-km) radius of the site.
The terrain category and roof exposure condition chosen shall be representative of the anticipated conditions during the life
of the structure. An exposure factor shall be determined for each roof of a structure.
*Definitions:
Partially exposed: All roofs except as indicated below.
Fully exposed: Roofs exposed on all sides with no shelter† afforded by terrain, structures, or trees. Roofs that contain several
large pieces of mechanical equipment, parapets that extend above the height of the balanced snow load (h b ), or other obstructions
are not in this category.
Sheltered: Roofs located tight in among conifers that qualify as obstructions.
†Obstructions within a distance of 10h o provide “shelter,” where h o is the height of the obstruction above the roof level. If
the only obstructions are a few deciduous trees that are leafless in winter, the “fully exposed” category shall be used except for
terrain Category “A.” Note that these are heights above the roof. Heights used to establish the terrain category in Sec. 6.5.3 are
heights above the ground.
Source: From Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other Structures, SEI/ASCE 7-02, American Society of Civil
Engineers, Reston, Va., with permission.
TABLE 4.7 Thermal Factor C t
Thermal condition* C t
All structures except as indicated below 1.0
Structures kept just above freezing and others with cold, ventilated roofs in which 1.1
the thermal resistance (R/value) between the ventilated space and the heated space exceeds
2
2
25°F⋅h⋅ft /Btu (4.4 K⋅m /W)
Unheated structures and structures intentionally kept below freezing 1.2
Continuously heated greenhouses† with a roof having a thermal resistance (R-value) less than 0.85
2
2
2.0°F⋅h⋅ft /Btu (0.4 K⋅m /W)
*These conditions shall be representative of the anticipated conditions during winters for the life of the structure.
†Greenhouses with a constantly maintained interior temperature of 50°F (10°C) or more at any point 3 ft above the floor level
during winters and having either a maintenance attendant on duty at all times or a temperature alarm system to provide warning
in the event of a heating failure.
Source: From Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other Structures, SEI/ASCE 7-02, American Society of Civil
Engineers, Reston, Va., with permission.
TABLE 4.8 Importance Factor for Snowloads, Eq. (4.3)
Category* Importance factor I
I 0.8
II 1.0
III 1.1
IV 1.2
*See Table 4.10 for description of categories.
Source: From Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other
Structures, SEI/ASCE 7-02, American Society of Civil Engineers,
Reston, Va., with permission.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.