Page 79 - Structural Steel Designers Handbook AISC, AASHTO, AISI, ASTM, and ASCE-07 Design Standards
P. 79
Brockenbrough_Ch03.qxd 9/29/05 5:05 PM Page 3.11
CONNECTIONS
CONNECTIONS 3.11
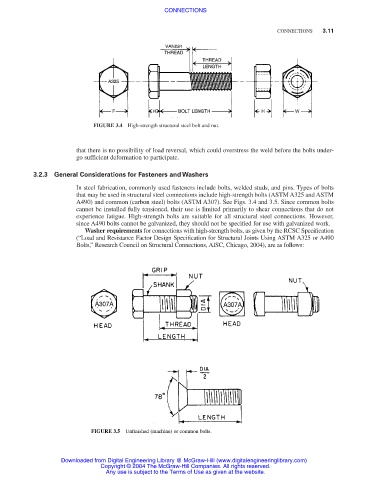
FIGURE 3.4 High-strength structural steel bolt and nut.
that there is no possibility of load reversal, which could overstress the weld before the bolts under-
go sufficient deformation to participate.
3.2.3 General Considerations for Fasteners and Washers
In steel fabrication, commonly used fasteners include bolts, welded studs, and pins. Types of bolts
that may be used in structural steel connections include high-strength bolts (ASTM A325 and ASTM
A490) and common (carbon steel) bolts (ASTM A307). See Figs. 3.4 and 3.5. Since common bolts
cannot be installed fully tensioned, their use is limited primarily to shear connections that do not
experience fatigue. High-strength bolts are suitable for all structural steel connections. However,
since A490 bolts cannot be galvanized, they should not be specified for use with galvanized work.
Washer requirements for connections with high-strength bolts, as given by the RCSC Specification
(“Load and Resistance Factor Design Specification for Structural Joints Using ASTM A325 or A490
Bolts,” Research Council on Structural Connections, AISC, Chicago, 2004), are as follows:
FIGURE 3.5 Unfinished (machine) or common bolts.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.