Page 579 - Sustainable Cities and Communities Design Handbook
P. 579
The Los Angeles Community College District Chapter j 27 547
guide,” and existing LACC specific data were collected. Given this, it is
estimated that within 5 years, LACC’s electrical energy consumption will
2
increase by almost 4,400,000 kWh, or approximately 13.63 kWh/ft .
The second program is a demand side management initiative aimed at
reducing the current load burden, with the energy savings paying for capital
investment of the energy-saving technologies. This involves examining the
current energy infrastructure in place at LACC and making recommendations
on how to reduce the energy demand. In Jun. 2009, a 3-month comprehensive
energy analysis for LACC was completed. This involved evaluating each
building on the LACC campus according to the following criteria:
l Age
l Condition
l Performance
l Lighting system, including controls and fixtures
l Building automation
l Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems
l Equipment upgrades
l Ability to connect to a central plant
l Structural upgrades
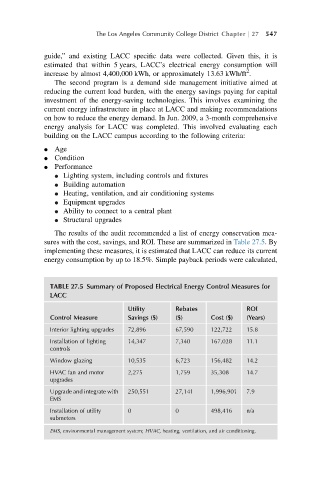
The results of the audit recommended a list of energy conservation mea-
sures with the cost, savings, and ROI. These are summarized in Table 27.5.By
implementing these measures, it is estimated that LACC can reduce its current
energy consumption by up to 18.5%. Simple payback periods were calculated,
TABLE 27.5 Summary of Proposed Electrical Energy Control Measures for
LACC
Utility Rebates ROI
Control Measure Savings ($) ($) Cost ($) (Years)
Interior lighting upgrades 72,896 67,590 122,722 15.8
Installation of lighting 14,347 7,340 167,028 11.1
controls
Window glazing 10,535 6,723 156,482 14.2
HVAC fan and motor 2,275 1,759 35,308 14.7
upgrades
Upgrade and integrate with 250,551 27,141 1,996,901 7.9
EMS
Installation of utility 0 0 498,416 n/a
submeters
EMS, environmental management system; HVAC, heating, ventilation, and air conditioning.