Page 357 - Sustainable On-Site CHP Systems Design, Construction, and Operations
P. 357
330 Ca s e S t u d y 1
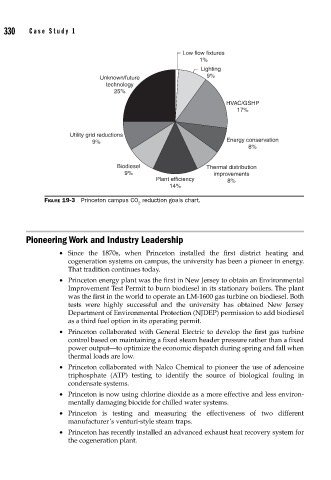
Low flow fixtures
1%
Lighting
Unknown/future 9%
technology
25%
HVAC/GSHP
17%
Utility grid reductions
9% Energy conservation
8%
Biodiesel Thermal distribution
9% improvements
Plant efficiency 8%
14%
FIGURE 19-3 Princeton campus CO reduction goals chart.
2
Pioneering Work and Industry Leadership
• Since the 1870s, when Princeton installed the first district heating and
cogeneration systems on campus, the university has been a pioneer in energy.
That tradition continues today.
• Princeton energy plant was the first in New Jersey to obtain an Environmental
Improvement Test Permit to burn biodiesel in its stationary boilers. The plant
was the first in the world to operate an LM-1600 gas turbine on biodiesel. Both
tests were highly successful and the university has obtained New Jersey
Department of Environmental Protection (NJDEP) permission to add biodiesel
as a third fuel option in its operating permit.
• Princeton collaborated with General Electric to develop the first gas turbine
control based on maintaining a fixed steam header pressure rather than a fixed
power output—to optimize the economic dispatch during spring and fall when
thermal loads are low.
• Princeton collaborated with Nalco Chemical to pioneer the use of adenosine
triphosphate (ATP) testing to identify the source of biological fouling in
condensate systems.
• Princeton is now using chlorine dioxide as a more effective and less environ-
mentally damaging biocide for chilled water systems.
• Princeton is testing and measuring the effectiveness of two different
manufacturer’s venturi-style steam traps.
• Princeton has recently installed an advanced exhaust heat recovery system for
the cogeneration plant.