Page 353 - Sustainable On-Site CHP Systems Design, Construction, and Operations
P. 353
326 Ca s e S t u d y 1
burn natural gas, while the boilers and gas turbine are capable of firing natural gas or
diesel fuel.
The boilers are approximately 83 percent efficient when firing using natural gas and
87 percent when firing with No. 2 diesel fuel. The duct firing process is approximately
82 percent efficient. The boilers were installed in 1996.
Steam Distribution and Condensate Collection
Steam at 225 psig is delivered to the steam turbines in the chilled water plant for use in
chilled water production. Additional steam is delivered to the campus to serve space
heating and research needs. Main steam pressure is 220 psig. This is reduced to 45 to
90 psig in the distribution system, and dropped below 15 psig at each building entrance.
The campus steam distribution network consists of insulated carbon steel piping in
small steam and condensate tunnels and larger multiutility walk-through tunnels.
Some condensate piping is direct buried. Condensate is pumped back to the plant with
typical recovery of 75 to 85 percent. This high rate of recovery results in a minimum of
water, chemical, and thermal waste.
An ongoing condensate recovery improvement program involving plant opera-
tions, campus maintenance, and facilities engineering staff identifies problems and
targets areas of opportunity to improve the campus condensate recovery rate. In recent
years, this program has lead to the repair or replacement of dozens of condensate pumps,
added thermal insulation to thousands of feet of pipe, tested and planned replacement
and upgraded hundreds of steam traps.
Chilled Water Production
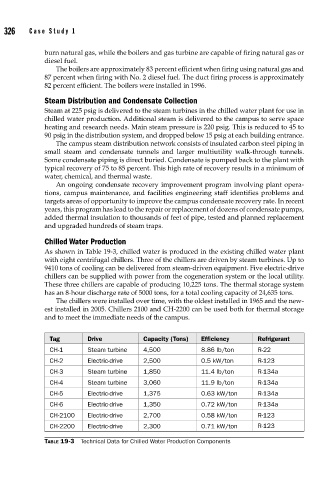
As shown in Table 19-3, chilled water is produced in the existing chilled water plant
with eight centrifugal chillers. Three of the chillers are driven by steam turbines. Up to
9410 tons of cooling can be delivered from steam-driven equipment. Five electric-drive
chillers can be supplied with power from the cogeneration system or the local utility.
These three chillers are capable of producing 10,225 tons. The thermal storage system
has an 8-hour discharge rate of 5000 tons, for a total cooling capacity of 24,635 tons.
The chillers were installed over time, with the oldest installed in 1965 and the new-
est installed in 2005. Chillers 2100 and CH-2200 can be used both for thermal storage
and to meet the immediate needs of the campus.
Tag Drive Capacity (Tons) Efficiency Refrigerant
CH-1 Steam turbine 4,500 8.86 lb/ton R-22
CH-2 Electric-drive 2,500 0.5 kW/ton R-123
CH-3 Steam turbine 1,850 11.4 lb/ton R-134a
CH-4 Steam turbine 3,060 11.9 lb/ton R-134a
CH-5 Electric-drive 1,375 0.63 kW/ton R-134a
CH-6 Electric-drive 1,350 0.72 kW/ton R-134a
CH-2100 Electric-drive 2,700 0.58 kW/ton R-123
CH-2200 Electric-drive 2,300 0.71 kW/ton R-123
TABLE 19-3 Technical Data for Chilled Water Production Components