Page 51 - Synthetic Fuels Handbook
P. 51
NATURAL GAS 39
and bears no relationship to the density of water). As a comparison, the density of liquefied
natural gas is approximately 0.41 to 0.5 kg/L, depending on temperature, pressure, and
composition; in comparison the density of water is 1.0 kg/L.
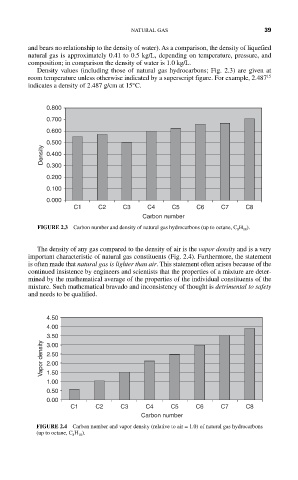
Density values (including those of natural gas hydrocarbons; Fig. 2.3) are given at
room temperature unless otherwise indicated by a superscript figure. For example, 2.487 15
indicates a density of 2.487 g/cm at 15°C.
0.800
0.700
0.600
0.500
Density 0.400
0.300
0.200
0.100
0.000
C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8
Carbon number
FIGURE 2.3 Carbon number and density of natural gas hydrocarbons (up to octane, C 8 H 18 ).
The density of any gas compared to the density of air is the vapor density and is a very
important characteristic of natural gas constituents (Fig. 2.4). Furthermore, the statement
is often made that natural gas is lighter than air. This statement often arises because of the
continued insistence by engineers and scientists that the properties of a mixture are deter-
mined by the mathematical average of the properties of the individual constituents of the
mixture. Such mathematical bravado and inconsistency of thought is detrimental to safety
and needs to be qualified.
4.50
4.00
3.50
Vapor density 2.50
3.00
2.00
1.50
1.00
0.50
0.00
C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8
Carbon number
FIGURE 2.4 Carbon number and vapor density (relative to air = 1.0) of natural gas hydrocarbons
(up to octane, C 8 H 18 ).